In the following post we compare the features of 4 top risk management apps on Jira Server. Comparison of risk management apps on Jira Cloud can be viewed here.
There are four popular apps on Jira Server for risk management purposes. Two of them are for product risk management and the other two for project risk management purposes.
The product risk management apps (SoftComply Risk Manager and SoftComply Risk Manager Plus) have been developed with safety critical product risk requirements in mind as they follow the requirements specified in ISO 14971 yet customizable to any software product risk management project. You can read more about the safety critical product risk management requirements here.
The project risk management apps (Risk Register and Risk Management for Jira) have been developed for managing project and organizational risks in mind, where the former is based on ISO 31000 risk management process and the latter is a more generic risk management app.
Following is a closer look at each of the four apps to provide you an overview of the main use cases of each of them, their risk management methods, risk visualization options, and their risk measurement, risk mitigation, risk traceability and risk reporting functionalities as well as an overview of their ease of use.
To compare the features of each of the four risk management apps, we first provide an overview of them in the table below. To learn more about each of the apps and their features, please continue reading after the table.
Comparison of the Best Risk Management Apps on Jira Server
SoftComply Risk Manager |
Risk Register |
SoftComply Risk Manager PLUS |
Risk Management for Jira |
|
Main Use Cases |
Product/software/device risk management
Safety-critical product risk management for regulated industries e.g. medical devices, space, engineering, aviation, defence industries |
Project risk management
organizational risk management |
Product/software/device risk management
Safety-critical product risk management for e.g. medical device industry, space, aviation, defence , automotive industries |
Project risk management |
Risk Management Method |
Hazard Analysis template based on ISO 14971 | Risk management template based on ISO 31000 | Hazard Analysis & FMEA templates based on ISO 14971 | Generic risk management template |
Risk Visualisation |
Risk Matrices view (Initial and Residual) and the Risk table view | Risk Matrix view (Inherent and Residual) and Risk Register view | a) Risk Matrices (Initial and Residual)
or b) Risk Prioritization Number with Risk Levels, and Risk table views |
Risk Matrix and Risk board view |
Risk Measurement |
Risk Classes (based on the user configured risk matrices)
Risk Severity x Risk Probability |
Risk Classes (based on the user configured matrix)
Risk Impact x Risk Probability |
Either Risk Classes (matrices) or RPNs (Risk Prioritization Numbers)
a) Risk Severity x Risk Probability (Hazard Analysis); b) Risk Severity x Risk Occurrence x Risk Detectability (FMEA); c) Risk Severity x Risk Occurrence (FMEA) |
Risk Score as multiplication of Risk Consequence and Risk Likelikood
Risk Consequence x Risk Likelihood
|
Risk Mitigation |
Users can add links to mitigation and verification actions + additional links to related activities | Users can add one link to risk treatment | Users can add links to mitigation and verification actions + additional links to related activities | Users can add one link to risk treatment |
Risk Traceability |
Automated traceability between risks, requirement and test cases | No automated traceability | Automated traceability between risks, requirement and test cases | No automated traceability |
Risk Reporting |
Built in risk reports – ISO 14971 compliant Risk Plan and Risk Report + risk exporting features for both the table and matrices view | Dashboard gadget displays risk matrix view | Built in risk reports – ISO 14971 compliant Risk Plan and Risk Report + risk exporting features for both the table and matrices view | Risk table view |
Ease of Use |
Table and matrices views are fully customizable by the users | Risk matrix and register views fully customizable by the users | Table and model views are fully customizable by the users | Customizable only by developers, only 3 risk classes allowed |
1. SoftComply Risk Manager
1.1. Main Use Cases
- software/product/device risk management,
- for safety and security risk management,
- for regulated industries,
- IT risk management,
- security risk management,
- Hazard Analysis based on ISO 14971 – medical device risk management.
1.2. Risk management method
Hazard Analysis
1.3. Risk Visualization
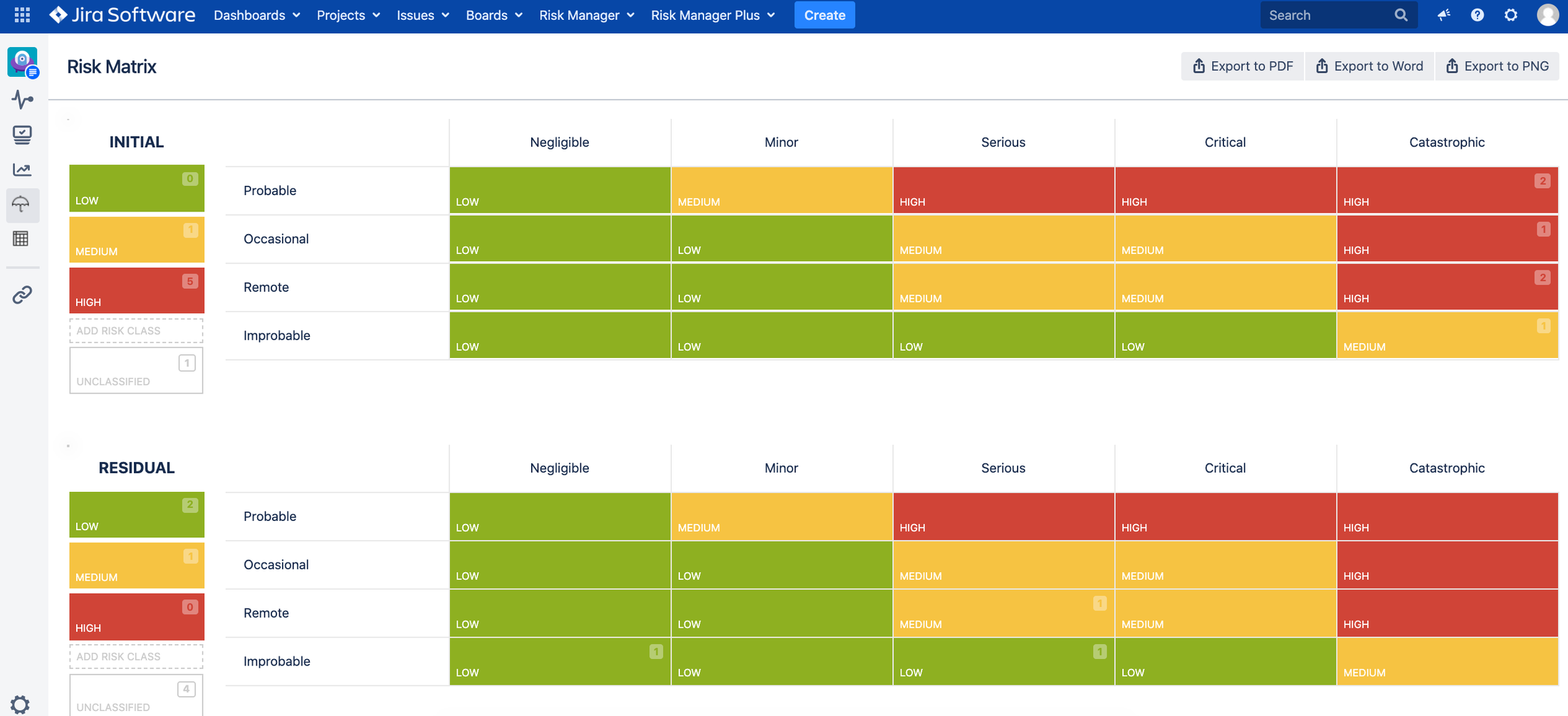
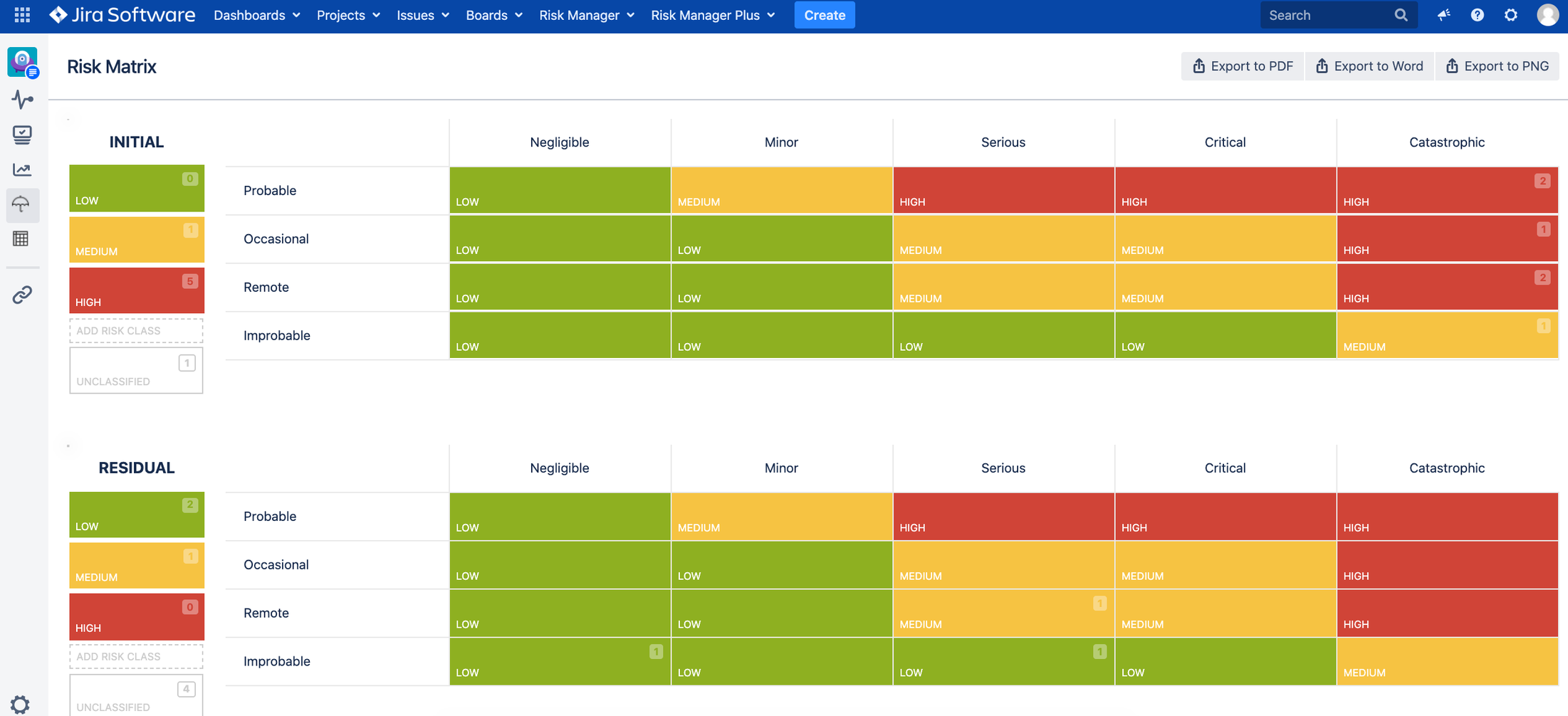
Two main risk management views:
1. Risk Matrices view – Initial and Residual Risk Matrix – user can customize the matrix size
and
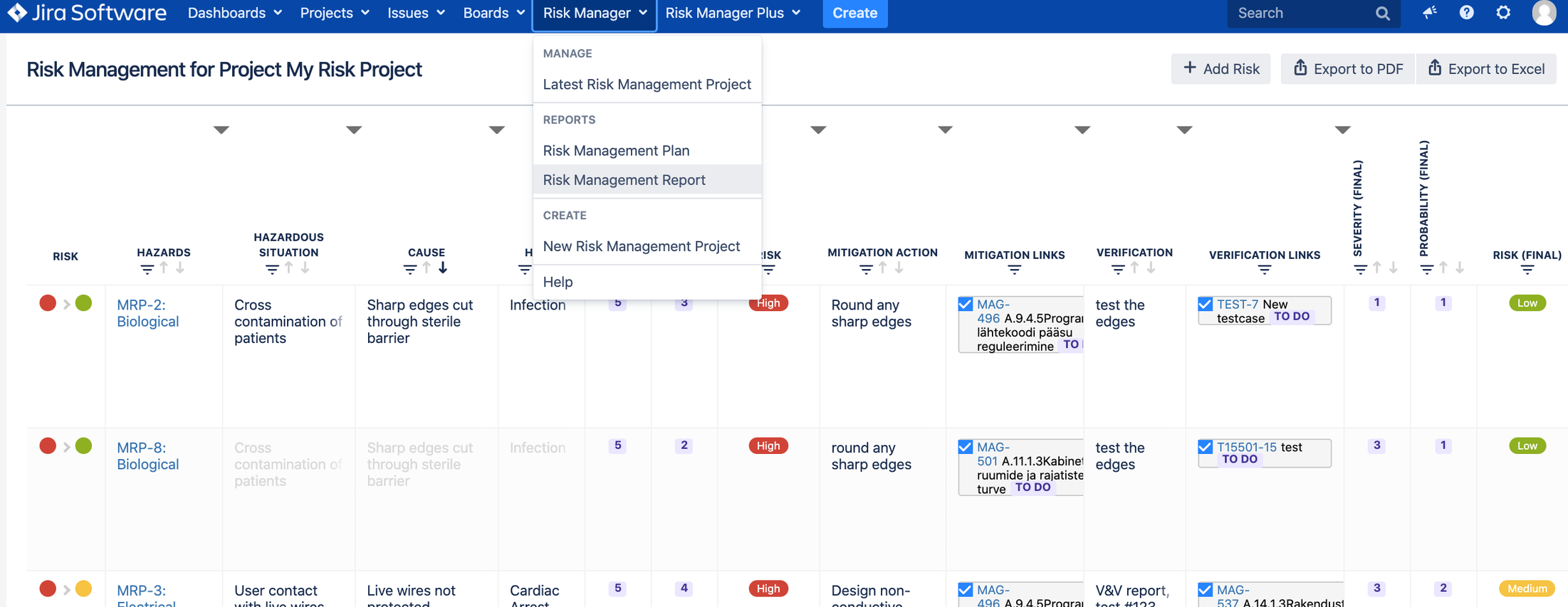
2. Risk Management Table view for all risk related information + automated traceability
1.4. Risk Measurement
Risk Class = Risk Severity x Risk Probability
1.5. Risk Mitigation
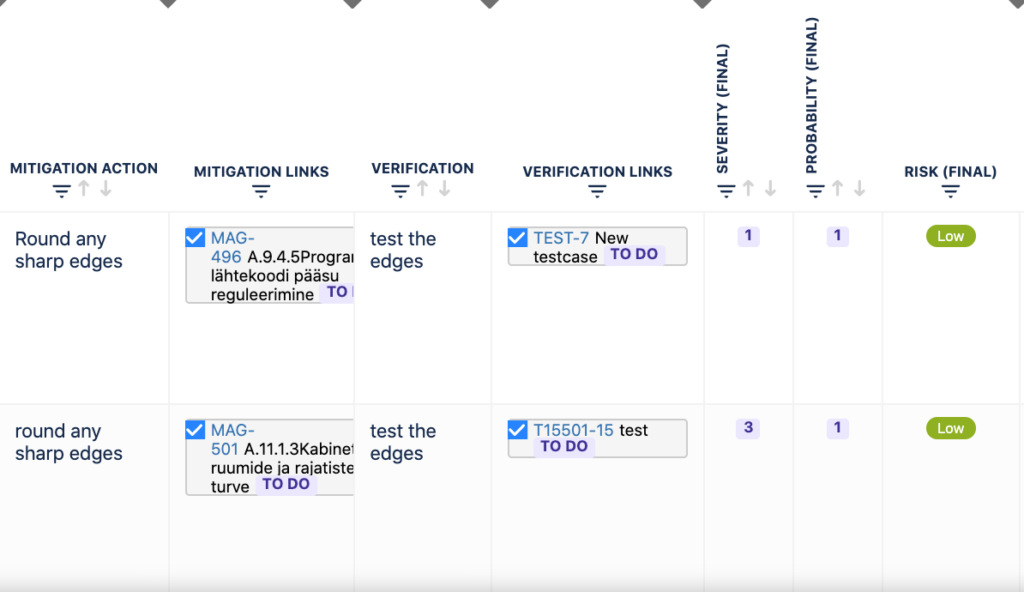
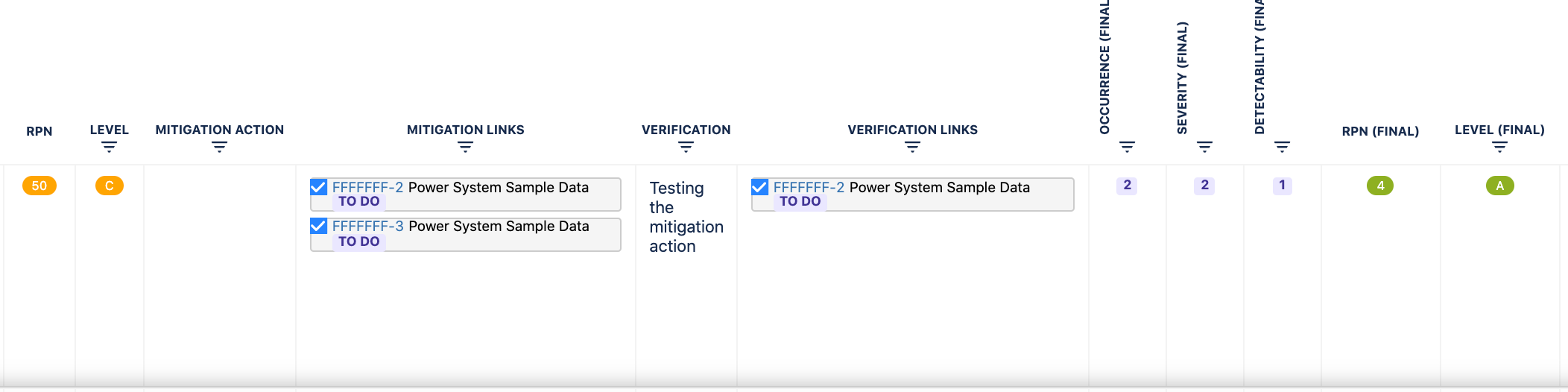
Users can add Mitigation actions and Verification actions as links to each risk.
1.6. Risk Traceability
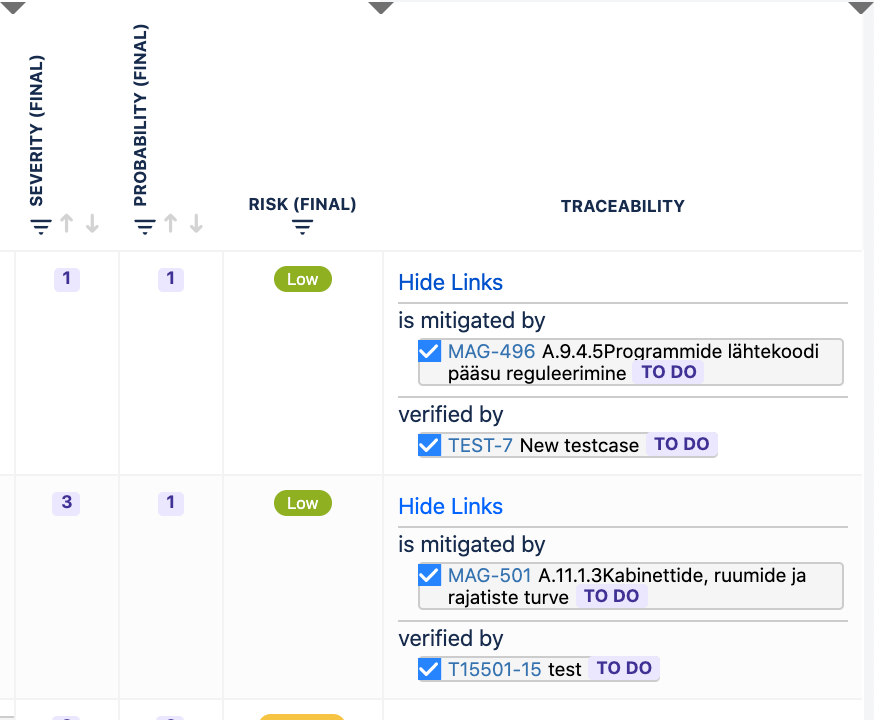
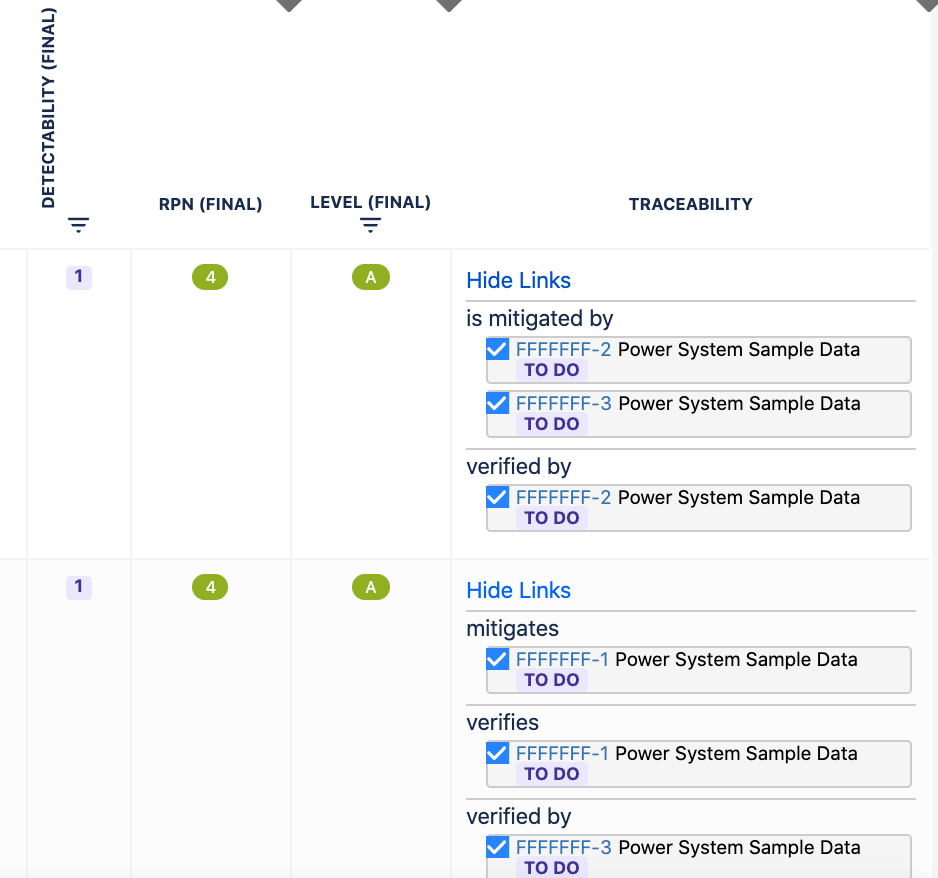
Builds automated traceability between requirements, risks and test cases visible in Risk Table view in “traceability” column.
1.7. Customization
Full customization of risk matrices (user can add risk severity and probability levels as well as risk classes) and risk table (user can import, export, add, edit, delete, move, filter and sort risk data in the table view).
1.8. Reporting
Integrated custom report templates for Risk Plan and Risk Report based on ISO 14971 requirements.
1.9. Ease of Use
- Previous risks can be copied with ‘clone risk’ functionality.
- Risk matrix and risk table views can be fully customized.
- Integrated reports for risk matrix and risk table view.
- Exporting of risk matrix and risk table into various formats.
SoftComply Risk Manager on Atlassian Marketplace
2. SoftComply Risk Manager Plus
2.1. Main Use Cases
- software/product/device risk management,
- for safety and security risk management,
- for the regulated industries like aviation, space, medical and automotive industries,
- IT risk management,
- FMEA and Hazard Analysis based on ISO 14971.
2.2. Risk management methods
Hazard Analysis & FMEA
2.3. Risk Visualization
a. Risk Matrices view – Initial and Residual Risk Matrix:
or
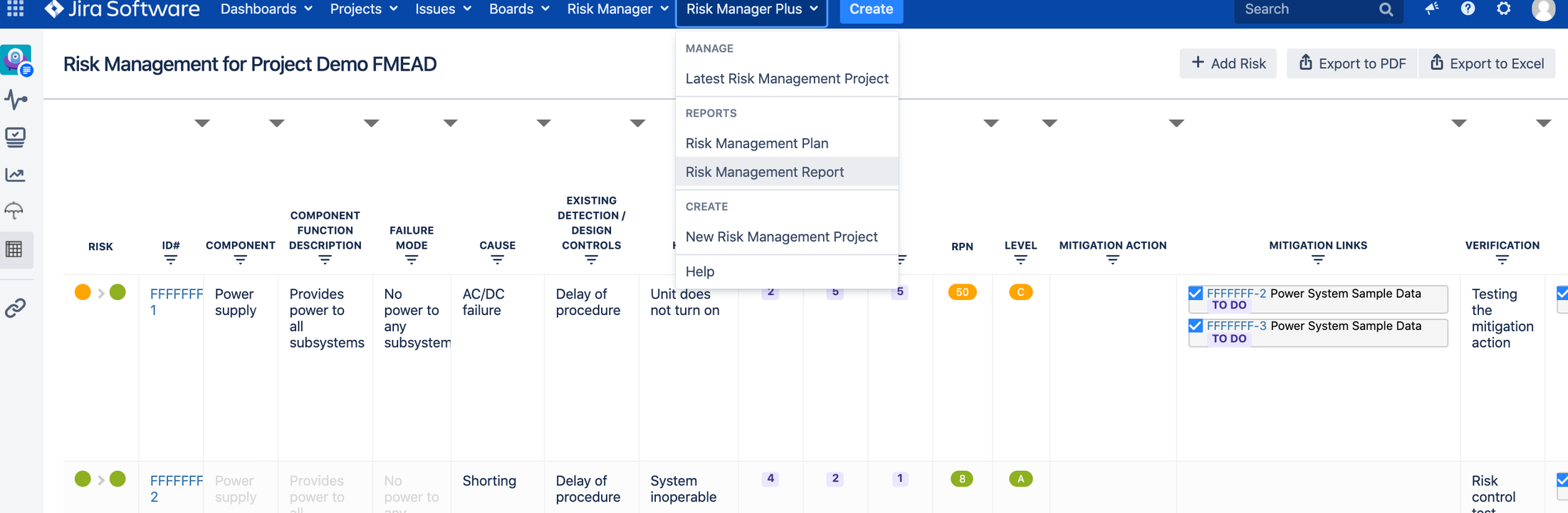
b. Risk Prioritization Numbers (RPN) view with Risk Levels:
and
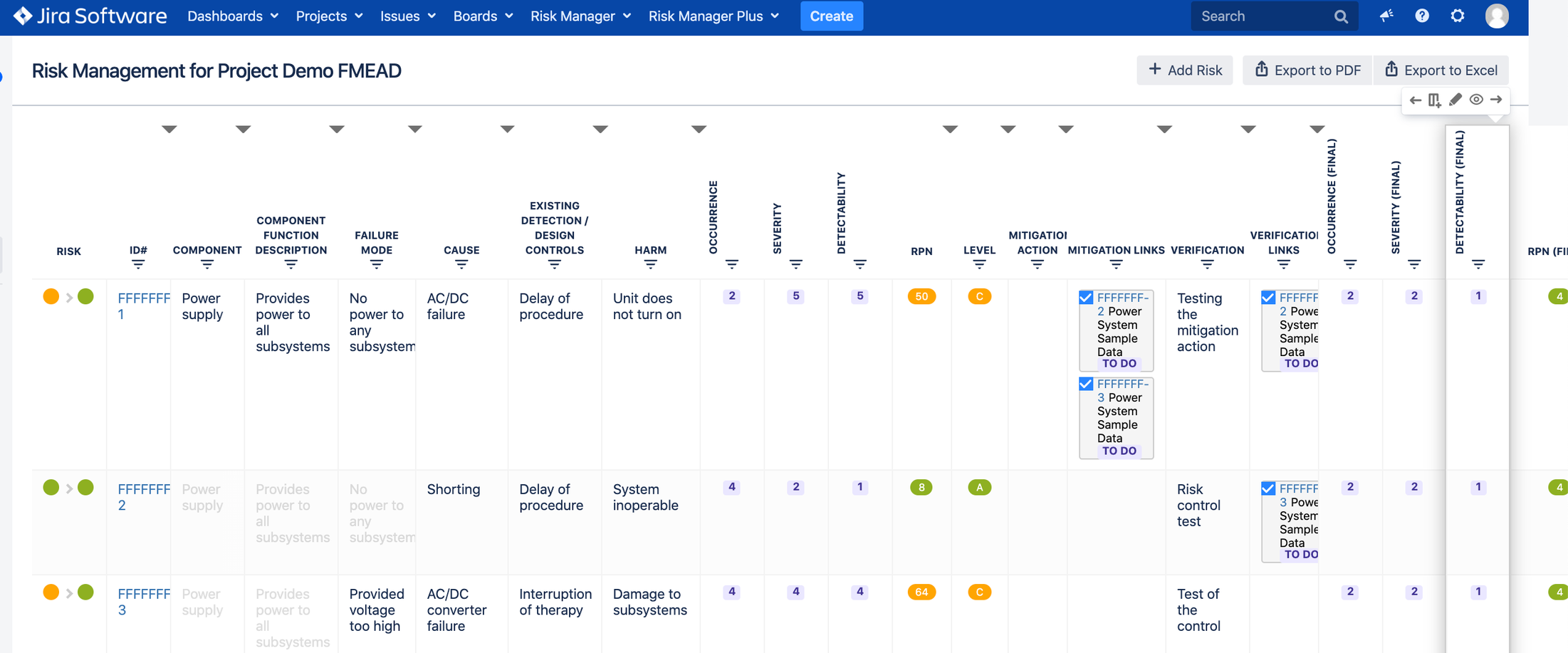
c. Risk Management Table view for all risk details. Example below for FMEA:
2.4. Risk Measurement
a. Risk Class = Risk Severity x Risk Probability/Occurrence (Hazard Analysis or FMEA); and
b. RPN (Risk Prioritization Number) = Risk Severity x Risk Occurrence x Risk Detectability (FMEA)
2.5. Risk Traceability
Automated traceability between requirements, risks and test cases:
2.6. Risk Mitigation
You can add Mitigation actions and Verification actions as links to each risk.
2.7. Customization
Full customization of risk matrices (user can customize all risk parameters as well as risk classes and RPN levels) and risk table (user can import, export, add, edit, delete, move, filter and sort risk data in the table view).
2.8. Reporting
Integrated custom report templates for Risk Plan and Risk Report based on ISO 14971 requirements.
2.9. Ease of Use
- Previous risks can be copied with ‘clone risk’ functionality.
- Risk matrix and risk table views can be fully customized.
- Integrated reports for risk matrix and risk table view.
- Exporting of risk matrix and risk table into various formats.
3. Risk Register
3.1. Main use cases
- Project risk management
- Based on ISO 31000
- Also for organizational risk management and governance
3.2. Risk Management method
Risk Management process based on ISO 31000
3.3. Risk Visualization
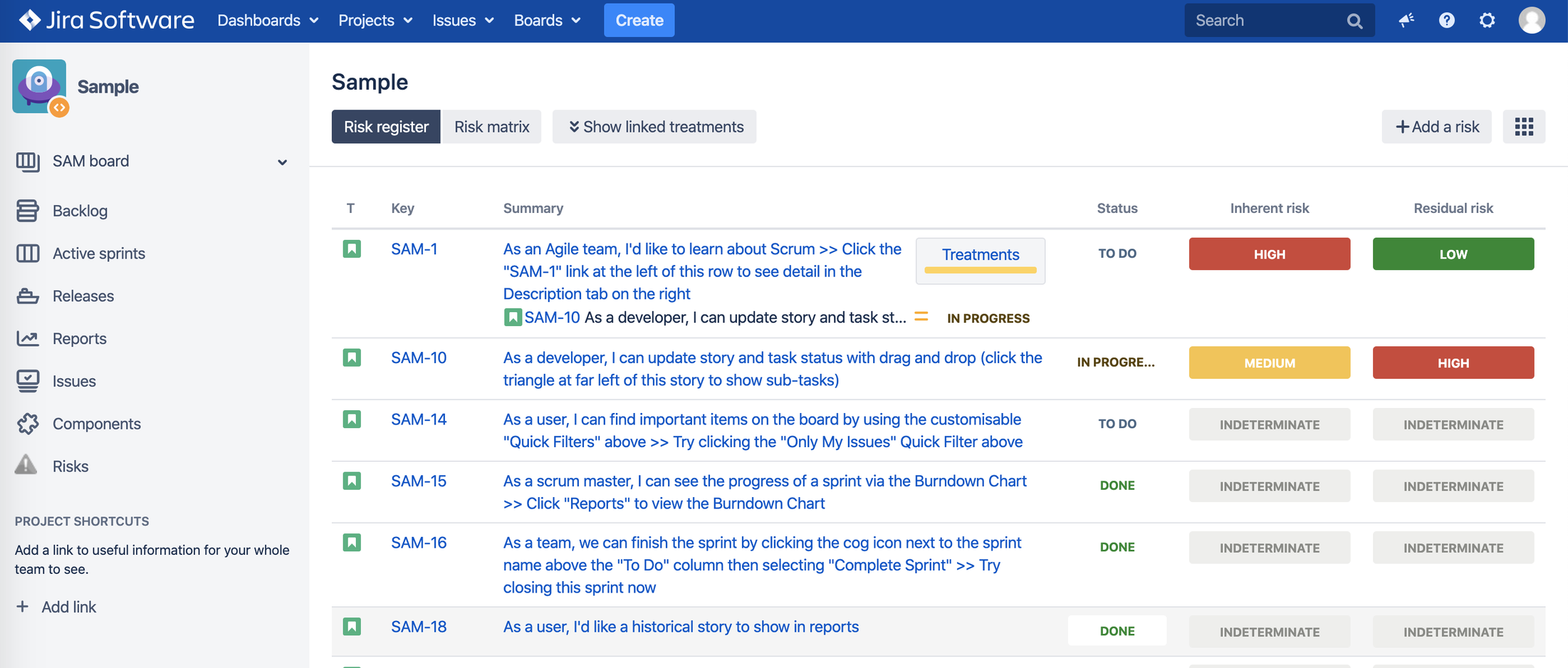
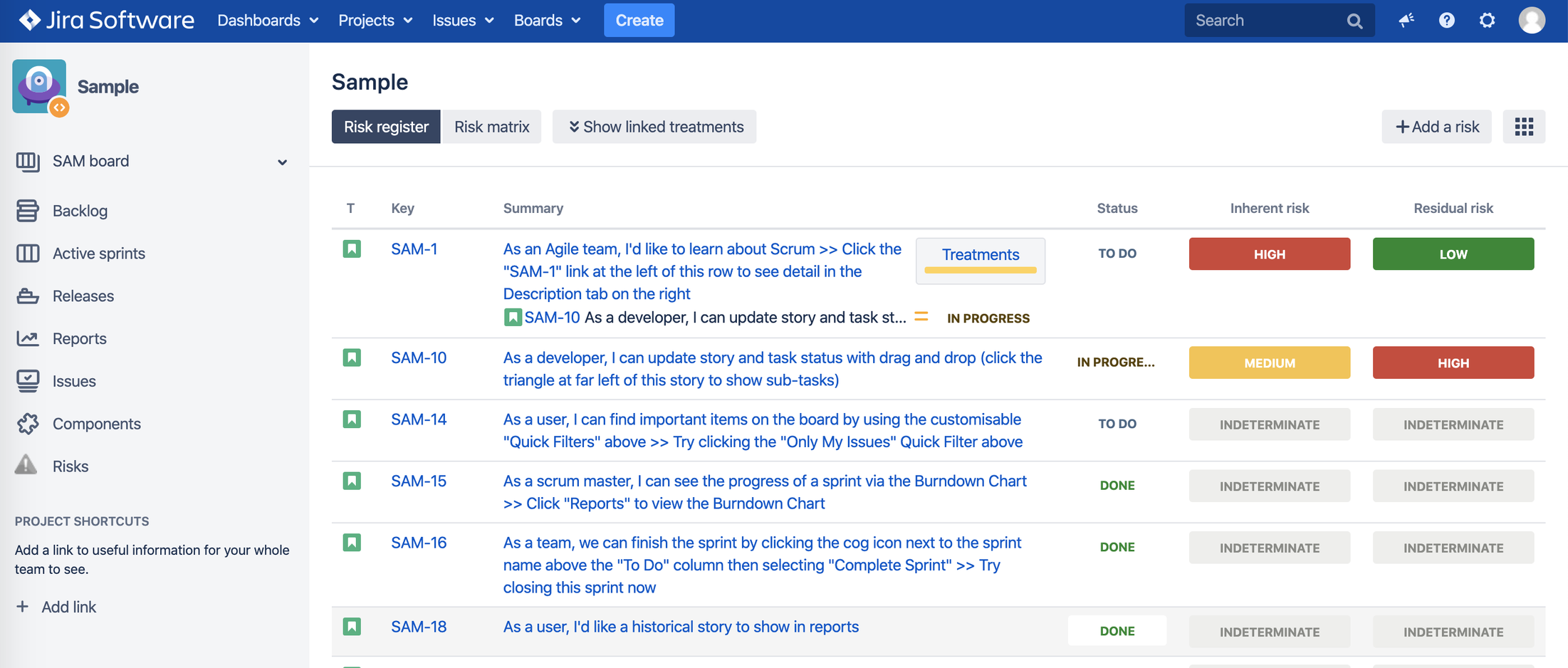
a. Risk Register – a board for risks with their risk classes and a link to risk treatment
and
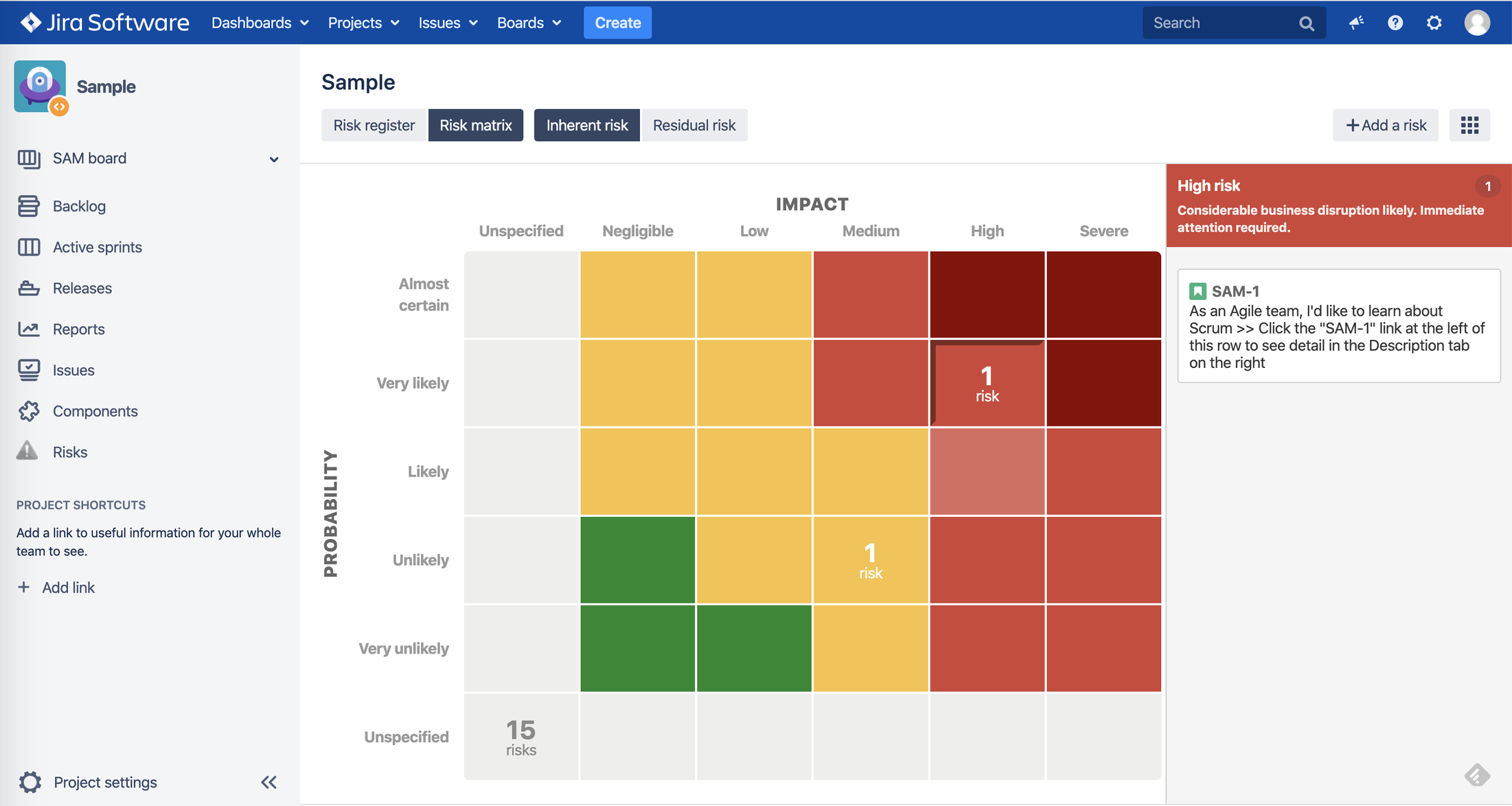
b. Risk Matrices view – user can see one risk matrix at a time
3.4. Risk Measurement
Risk Impact x Risk Probability as seen in Jira issue view:
3.5. Risk Mitigation
Users can add risk treatment/mitigation as Jira issue links to each risk.
3.6. Risk Traceability
No automated traceability between requirements, risks and test cases.
3.7. Reporting
- Dashboard gadget displays the risk matrix view.
- No built-in automated reporting.
- No automated traceability between risks, requirements and test cases.
- No built-in exporting.
3.8. Ease of Use
- Risk parameters and risk classes customizable in Jira issue view.
- Risk summary seen in risk matrix view.
- A previously configured risk matrix can be used in different projects.
Risk Register on Atlassian Marketplace
4. Risk Management for Jira
4.1. Main use cases
- Project risk management
4.2. Risk Management method
Risk Index/Score is calculated as a multiplication of Risk Consequence and Risk Likelihood.
4.3. Risk Visualization
a. Risk Matrix view – user can select if they want to see a risk matrix or a velocity meter as seen below:
or
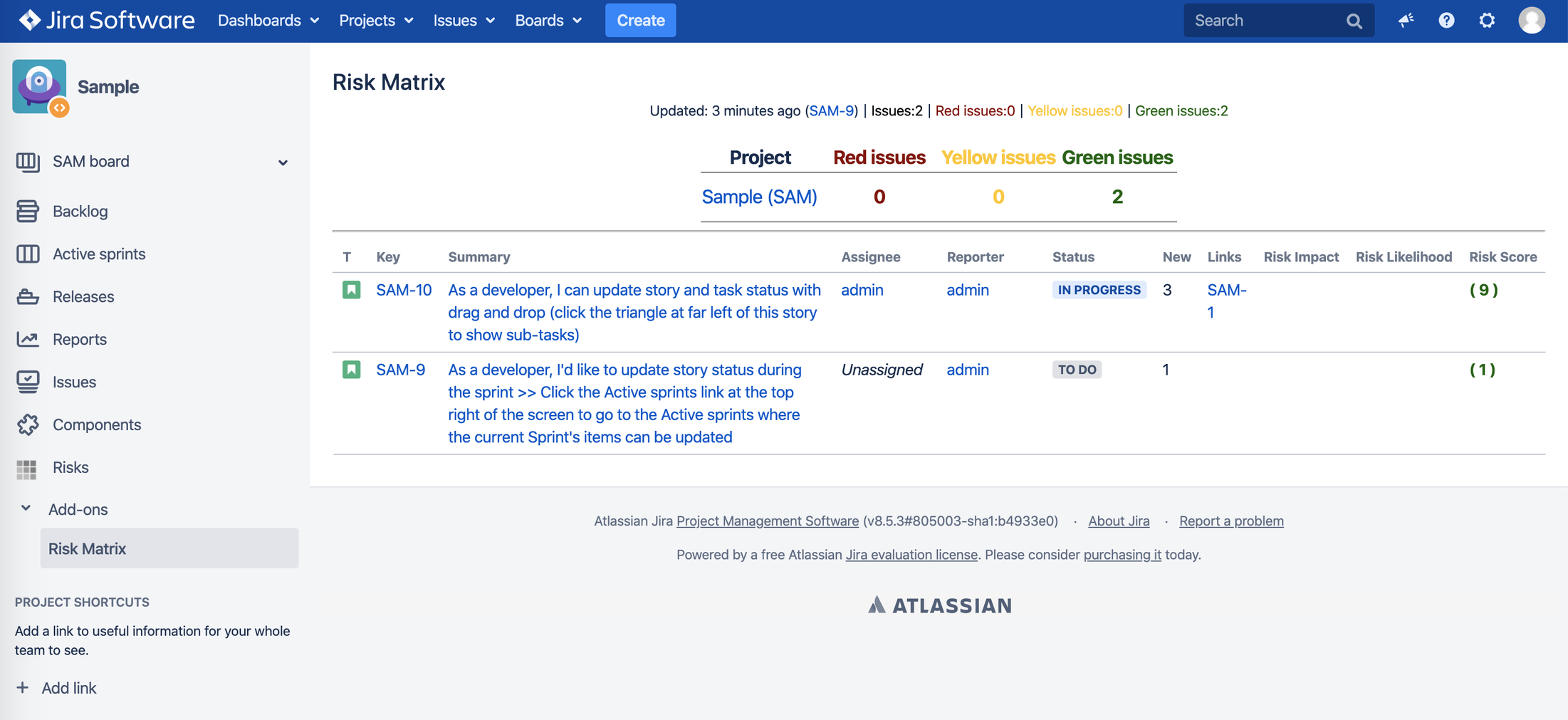
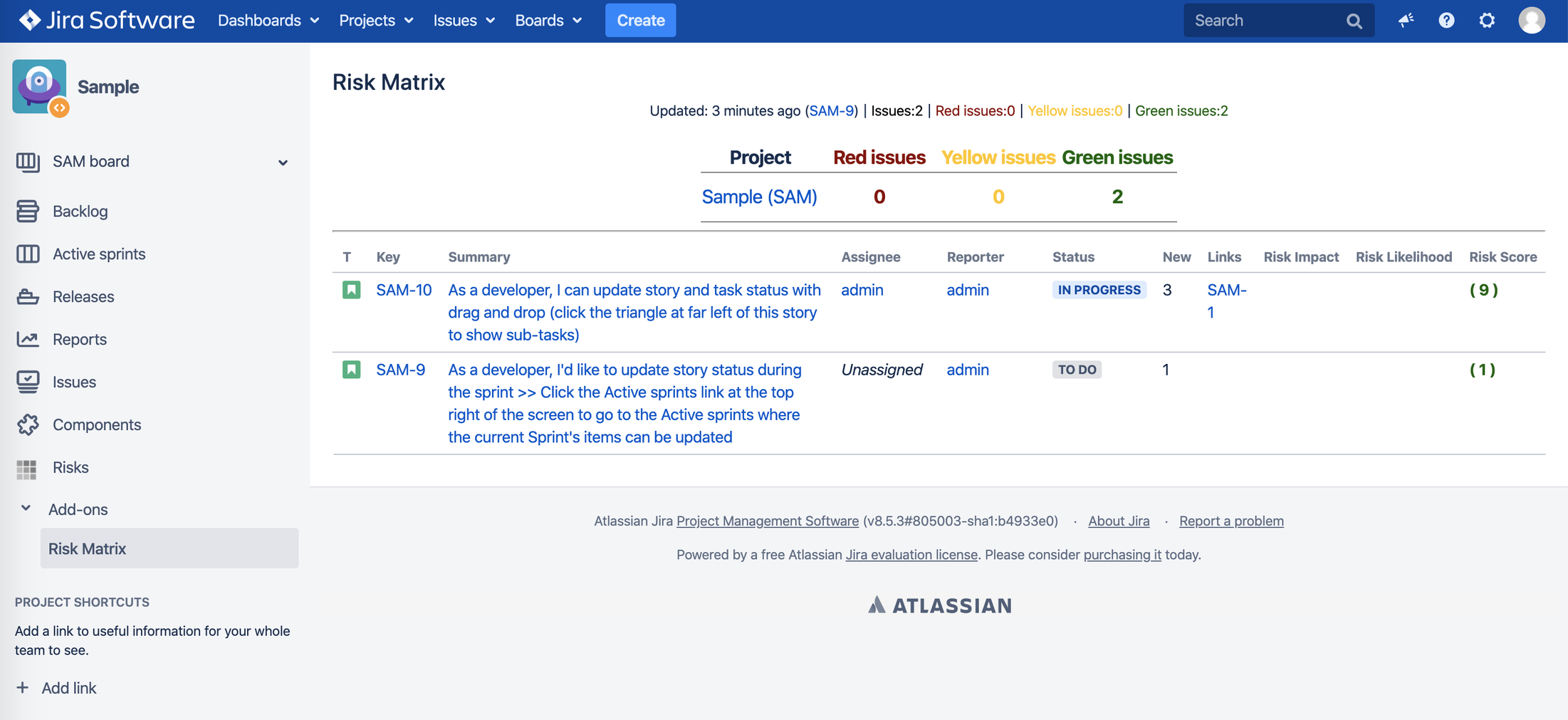
b. Risk board view – simple representation of risks with summary and risk likelihood, impact and risk score:
4.4. Risk Measurement
Risk Consequence x Risk Likelihood
4.5. Risk Mitigation
Users can add risk treatment/mitigation as Jira issue links to each risk.
4.6. Risk Traceability
No automated traceability but users can add one Jira issue link to each risk
4.7. Reporting
- Reports visualize the risk table view.
- No automated traceability between risks, requirements and test cases.
- No built-in exporting.
4.8. Ease of Use
- Although the risk matrix and board views are customizable, it requires some programming.
- There is a fixed number of risk classes – 3 classes allowed.
Risk Management for Jira on Atlassian Marketplace