A risk manager continuously identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential risks that could impact an organization’s objectives. They develop strategies to minimize threats, ensure compliance with regulations, and protect company’s financial stability and reputation.
Very often there is no one person called Risk Manager in an organisation. Risk management responsibilities are most typically shared between project or department managers or C-level executives.
The Evolution of Risk Management Roles

The role of Risk Management has changed significantly over the years. After World War II and up until the mid-1960s, risk management focused mainly on select losses and the role was often called an “insurance buyer”. Overtime the duties of a risk manager expanded to include loss prevention.
Today, risk managers focus primarily on risk perception, although the title and duties can vary between industries and organizations. Technology plays an increasingly important role now that AI and machine learning are taking over basic tasks, allowing risk managers to focus on the more creative value-adding activities and new areas of risk management.
Some experts believe that future risk managers will be either “engineers” who are tech-savvy and whose primary role is to implement controls early in development process, or “thinkers” who analyze data and provide insights for better decision making. Despite tech advancements, operational risks, especially in the regulated and safety-critical industries, remain the most important area of risk management due to potential harm products from these industries could cause humans.
The importance of risk managers is now more recognized than ever before. Post-Global Financial Crisis, many senior risk managers have moved to C-suite positions. Looking ahead, risk managers will be focusing more on strategic risks, organizational resilience, and new risk areas like cybersecurity and data protection.
Risk Manager: Roles & Responsibilities
A risk manager identifies, assesses, and mitigates risks that might impact an organization’s objectives, finances, and reputation. They create and implement risk management strategies, policies, and procedures to minimize threats and ensure compliance with regulations.
Key responsibilities most commonly include:
- Identifying all possible risks
- Conducting risk assessments
- Developing risk mitigation plans
- Monitoring and reporting risks continuously
- Communicating strategies throughout the organization
- Responding to unexpected events
Risk managers usually need strong analytical and effective communication skills, industry knowledge, adaptability, attention to detail, and great judgment.
What is Risk Based Management & its Benefits
Risk-based management is a strategic approach to managing an organization’s resources and decision-making processes based on risks. This methodology ensures that management focuses on the most significant risks that could impact the organization’s objectives and allocates resources to mitigate these risks effectively
There are several benefits to risk based management, like:
- Increased Preparedness and Business Resilience
Risk-based management is invaluable at a time of uncertainty, as they allow businesses to adapt more easily to changing conditions through a consistent and comprehensive approach to risk management. The risk-based methodology also forces organizations to look beyond the here and now to the emerging risks that will inevitably need to be tackled. - Eliminates Silo Mentality
The teams work together to assess risks, define key performance indicators, and monitor and resolve ongoing issues. Each group holds a different piece of the puzzle and Risk Based Approach helps connect the pieces to see the entire picture. It takes the entire team to ensure that product delivery is on time or ahead of schedule. With the Risk Based approach, all teams get access to a cross-functional risk assessment, leverage each other’s knowledge to ensure better quality. The result is better products with shorter timelines, increased efficiencies and controlled costs. - More Buy-in from Senior Management
Risk-based management involves a much more inclusive approach, where awareness about the risk process is raised across the organization through activities such as workshops and self-assessments. With senior management also closer to this process and understanding how other teams’ recommendations support the overall business objectives, they are more likely to appreciate the true value of everyone and take greater ownership of risk. - Higher Likelihood of Achieving Business Goals
Risk-based management promotes a proactive rather than reactive approach to managing potential issues, reducing the likelihood of unforeseen events causing major disruptions. It supports the achievement of business goals by fostering a structured, proactive, and informed approach to handling uncertainties and potential threats. This strategic focus on risks ensures that organizations can navigate challenges effectively and maintain their course toward their objectives. - Better Control over Organisational Assets
Further to the previous point, a risk-based approach combines all aspects of the risk universe which include objectives, risks, controls, processes, evaluations and reports. The relevance of any one aspect can be clearly viewed in relation to the entire risk management framework, such as the significance of a defective control or the risk that the control has been put in place to manage. This approach also means that it is apparent when a key objective is being threatened so that measures can be quickly established to mitigate the risk before it impacts the organization’s ability to achieve that objective.
Process of Risk Management
Risk Management process can be very detailed depending on the industry requirements and the types of risks that are being managed. On a high level, risk management follows the continuous loop of the 4 phases illustrated below where the output of each phase provides the necessary input to the next one.
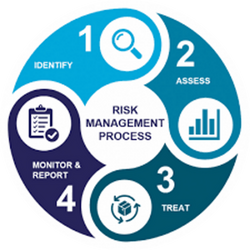
- Identification of Risks – systematically identify potential threats that could negatively impact the organization’s objectives
- Risk Assessment – evaluate the identified risks to understand their potential impact and likelihood, prioritizing them based on severity.
- Mitigation of Risks – develop and implement strategies to reduce or eliminate the likelihood and/or impact of the prioritized risks.
- Monitoring and Reporting Risks – continuously monitor and report risks to ensure that risk management strategies are effective and that new or evolving risks are promptly addressed.
Types of Risks
Risk managers handle various types of risks to keep the organization stable and successful. Here are key risk categories and how they are typically managed.

Financial Risks
These risks involve market fluctuations, currency exchange rates, credit risks, and liquidity risks. Risk managers develop strategies to mitigate these financial risks and protect the organization’s financial stability.
Operational Risks
These risks arise from daily operations, like supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, or human errors. Risk managers implement controls and procedures to minimize their impact on productivity and profitability.
Legal and Compliance Risks
Risk managers ensure the organization complies with laws, regulations, and industry standards. They monitor regulatory changes and develop strategies to mitigate non-compliance risks, which could lead to legal liabilities or reputational damage.
Strategic Risks
These risks relate to the organization’s long-term goals and decision-making. Risk managers assess the impact of competitive changes, market trends, and technological advancements, and help develop contingency plans.
Reputational Risks
Risk managers protect the organization’s brand by identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to negative publicity, such as data breaches or ethical violations. They create crisis management plans and communication strategies to minimize reputational impact.
Information Security Risks
Information security risks involve potential threats to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s data, which risk managers can assess by identifying vulnerabilities, evaluating potential impacts, and implementing controls to mitigate these threats.
Project Risks
These risks can affect the successful completion of a project. Risk managers continuously analyze project plans and identifying potential risks in the project budget, schedule or resources.
Product Risks
These risks may affect the quality, performance, or market success of a product, especially relevant in the regulated industries where products can reach the market only after a successful audit. Risk managers conduct Hazard Analysis and FMEA to identify any product risks and determine the mitigation actions to lower the risk to acceptable level.
By managing these risks, risk managers ensure the organization’s resilience and long-term success in a complex business environment.
Key Tools and Techniques in Risk Analysis

Risk analysis involves several tools and techniques to identify, assess, and prioritize risks. Here are some key ones:
Probability and Impact Matrix
Risk matrix visualizes risks based on their likelihood and impact, categorizing them into a grid for prioritization. Use the matrix when you need to prioritize multiple risks to focus on those that could have the most significant effect on the project’s objectives.
SWOT Analysis
This analysis is a strategic planning tool that assesses an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is best to use it during the early stages of project planning or strategic decision-making to gain a comprehensive understanding of internal and external factors affecting the project or business
Root Cause Analysis
Identifies underlying causes of risks, addressing issues at their source. Use root cause analysis after identifying recurring issues or significant incidents to prevent their reoccurrence.
Risk Registers
Centralized view of risk information, including descriptions, impacts, mitigation strategies, and ownership, for effective monitoring. You should use risk register throughout the project lifecycle to maintain a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of risk management activities.
Delphi Technique
A method that gathers and refines the insights of a panel of experts through multiple rounds of questionnaires to reach a consensus on risk identification and assessment. Used primarily when there is a need to achieve a reliable consensus on complex or uncertain risks.
Decision Tree Analysis
This is a visual and analytical tool used to map out decision pathways and their potential outcomes, including risks and rewards, helping to evaluate different risk mitigation options. Most often used when making complex decisions that involve multiple possible scenarios and outcomes.
Bow-Tie Analysis
A method that visualizes the pathways of a risk event, showing both preventive and mitigating controls to manage its causes and consequences. This method is used to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of risk management strategies for critical hazards.
Quantitative Tools
Tools like Monte Carlo Simulations and Cyber Risk Quantification use mathematical models for numerical risk assessments and decision-making. Most often used when precise, data-driven risk assessments are needed for decision-making.
Choosing the right tools depends on factors like the organization’s mission and the specific risks being addressed. Using these tools helps organizations identify, prioritize, and mitigate risks effectively.
The Role of Technology in Modern Risk Management

Technology is crucial in modern risk management. It helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks more effectively. Advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning analyze large data sets, uncover hidden patterns, and predict potential risks, allowing businesses to take proactive measures.
Real-time monitoring tools and automated alerts enable prompt risk identification and response, minimizing threats’ impact. Technology also streamlines compliance processes, enhances cybersecurity, and improves team collaboration.
Using integrated risk management platforms and advanced analytics, organizations can get a comprehensive view of risks, make data-driven decisions, and enhance resilience.
Emerging Trends in Risk Management

In 2024, several trends are shaping risk management. One major trend is the increasing complexity and interconnectedness of risks, driven by digital transformation and increasing amount of cybersecurity attacks. This demands a proactive, agile approach to risk management with real-time monitoring and mitigation.
Another trend is data-driven risk management. Organizations use advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning for deeper insights into risks and informed decision-making. Data security remains a priority as digital technologies create new vulnerabilities.
ESG risks are also gaining attention, with stakeholders expecting proactive management of environmental, social, and governance issues. Regulatory pressures around data privacy, climate disclosures, and AI use are adding to compliance burdens.
To navigate this complex landscape, companies invest in integrated risk management platforms, advanced analytics, and upskilling teams. Collaboration between risk managers and other functions is essential for embedding risk awareness into strategic planning and enhancing resilience.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Risk management is crucial for organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact their goals, finances, and reputation. It requires a proactive approach, with risk managers developing strategies, implementing controls, and monitoring various risk categories, including financial, operational, legal, strategic, and reputational risks.
The role of risk manager has evolved due to global instability, technological advancements, and the need for differentiation. As the business landscape gets more complex, risk managers must adapt to trends like data-driven risk management, cybersecurity threats, and ESG risks, using advanced tools for deeper insights and strategic decision-making.
Effective risk management protects organizations from threats, enhances resilience, and supports long-term objectives. By embedding risk awareness into the culture and fostering team collaboration, organizations can confidently navigate the changing risk landscape.





