Per ISO 14971,
“Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) are techniques by which an effect or consequences of individual components are systematically identified and is more appropriate as the design matures.“
We won’t go into the details of the FMEA, but often we were asked to explain when (and if / how) the Risk Prioritization Number (RPN) should be used.
The RPN is a numerical value that represents the “risk level” of a certain combination of input factors. These input factors are typically the Severity (S) of the risk and the Occurrence (O) of the risk. Sometimes the Detection (D) value is used in addition to Severity and Occurrence.
In its simplest form the RPN is calculated as follows:
RPN = O x S (x D, if used)
where O, S and D are in a linear scale ranging from 1 (lowest / best case) to typically 5 (highest / worst case).
The use of the RPN is exactly what the name says: prioritization, meaning that risks with higher RPN should receive more attention than the ones with a lower RPN. It can also be used to determine the acceptability of a risk, but this is a decision that each company or project team has to make itself.
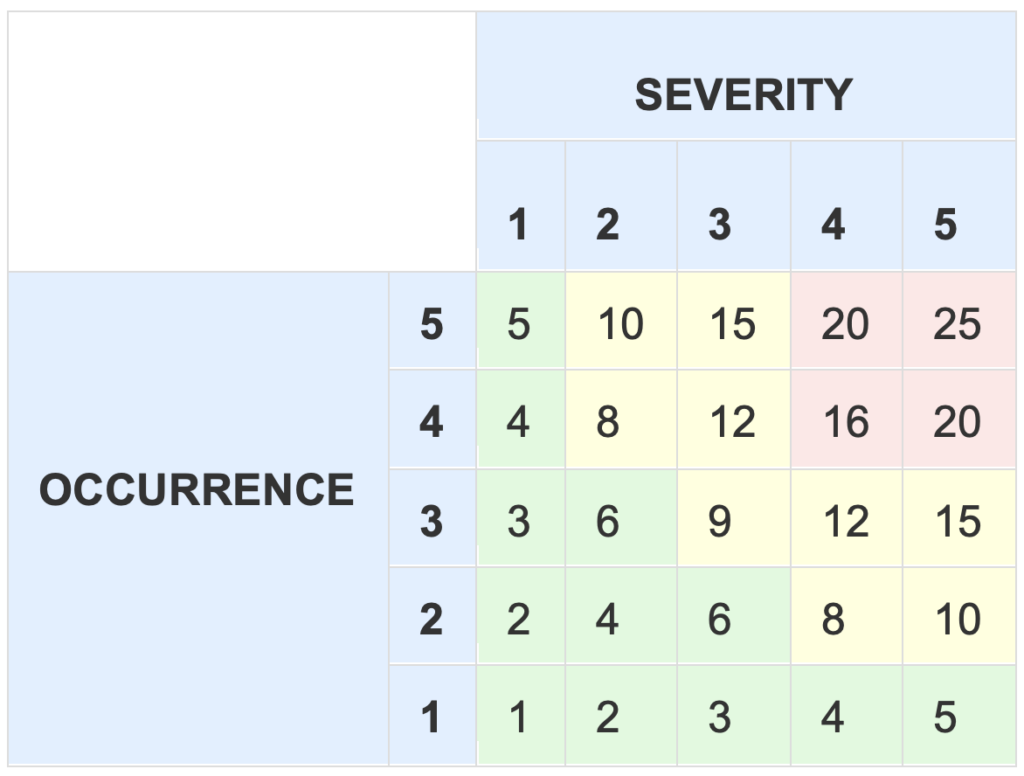
Here’s an example – in a typical scenario with only Occurrence and Severity, ranging from 1 to 5, the risk matrix looks like this:
|
SEVERITY |
||||||
|
1 |
2 | 3 | 4 |
5 |
||
|
OCCURRENCE |
5 |
5 |
10 |
15 | 20 | 25 |
|
4 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
|
|
3 |
3 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
15 |
|
|
2 |
2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
10 |
|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
5 |
|
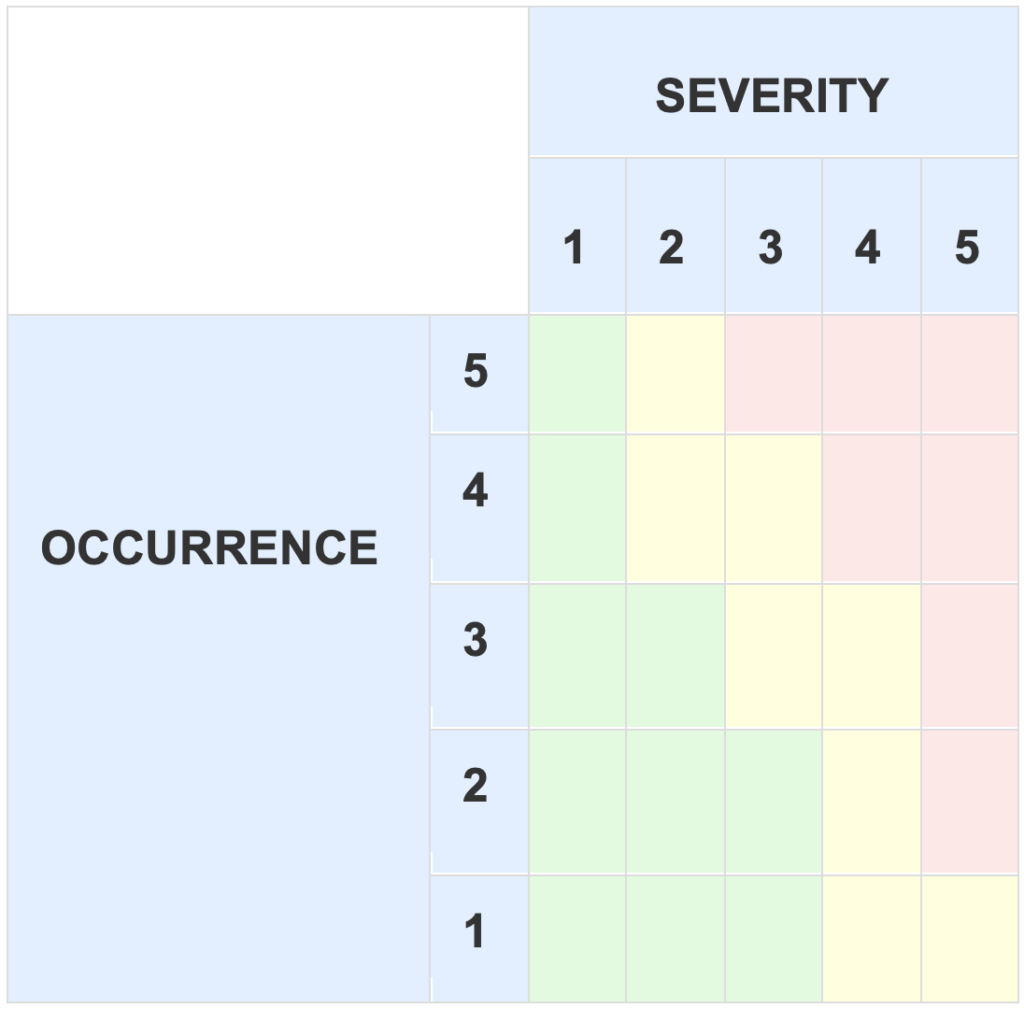
Once you have decided how to classify your RPNs (e.g. 1 to 7 = low, 8 to 15 = Med, 16 to 25 = High), then the matrix is automatically populated:
The RPN gives a quick solution regarding the acceptability of a risk, but often companies prefer to use the RPN as a “prioritization” tool only and to color the risk matrix according to other criteria or considerations, for example.
To summarize:
1. The use of the RPN in FMEAs is not mandated by ISO 14971; use it only when you think it’s beneficial to your analysis.
2. The RPN is not strictly related to the (un)acceptability of a risk, but it can be used for this purpose.
3. There is no unique formula to calculate the RPN. You can create your own for your specific product / project.
There is no general rule on how to classify your risk based on the RPN or other criteria, this is a decision that each company / project team have to make.
For simple product risk management in Atlassian Jira Cloud (with simple Risk Matrices), try out the SoftComply Risk Manager.
For a more advanced risk management app on Jira Cloud (with both Risk Matrices & RPNs), try out the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus.




