Risk Manager Plus User Guide
1. QUICK START GUIDE
- Install the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus from the Atlassian Marketplace to your Jira Server (or Data Center) instance. This step may require Jira administration permission.
- After the successful installation, click on the “Risk Manager Plus” item on the top navigation bar and select Create – New Risk Management Project from the drop-down menu.
- To create a new risk management project, follow these steps:
- Fill in the name of the project, the project key and the project lead;
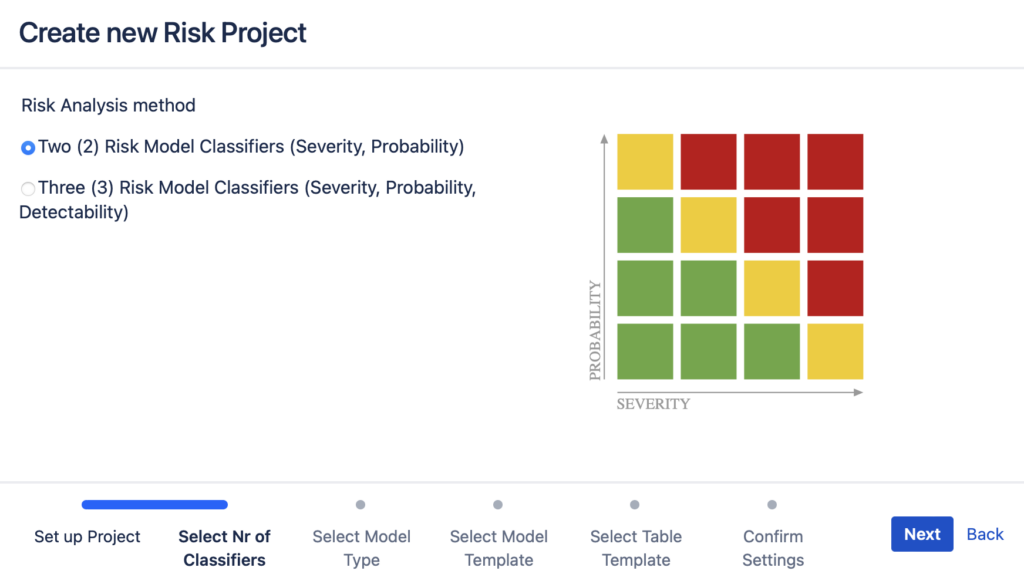
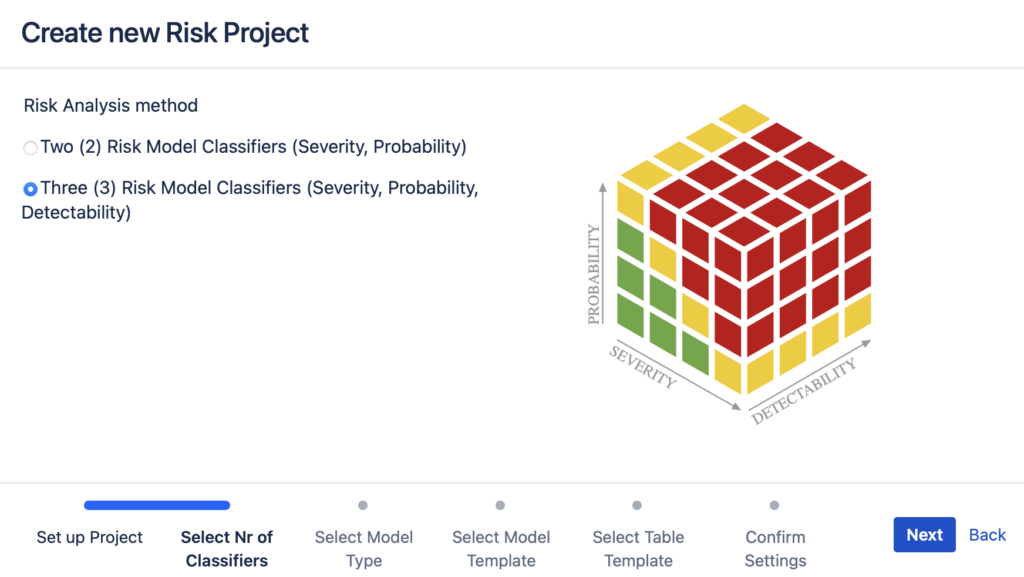
- Select the parameters you will use for risk assessment – Severity and Probability (2-parameters) or Severity, Probability and Detectability (3-parameters):
- If 2-parameter model is chosen, you can further define your Risk Matrix (4 pre-defined matrices available, these can be customized later, if necessary) size as a next step;
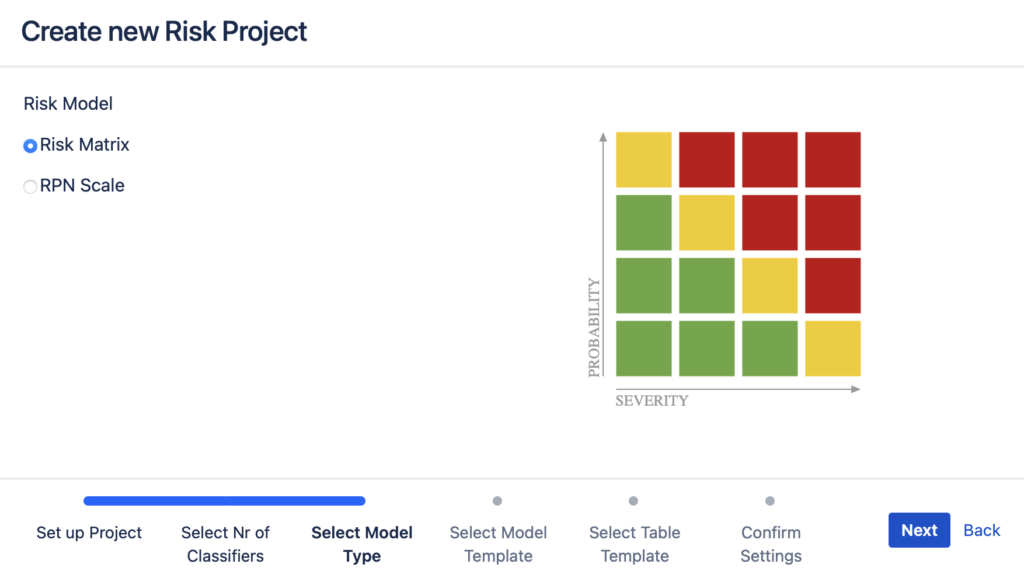
- In case of 3-parameter model, you can use either Risk Matrix method with Risk Levels or RPN (Risk Prioritisation Number) Scale;
- For RPN Scale, there are 4 scales built in but this can also be customized later, if necessary;
- Next, you can select from built in templates the layout of your Risk Table:
- A more general Product/Project risk management template;
- Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA);
- Hazard Analysis template;
- a Do It Yourself template (to build from scratch);
- Last step is to review the options you have chosen. If you are happy, click “Submit”.
Success! You have just created a new risk management project and you can now start managing risks in Jira.
NOTE! For compliant medical device risk management, there is a default setting where Harm and Severity are linked to each other (for Hazard Analysis and FMEA templates). You can change that in the Settings.
Here is a short video tutorial guiding you through these steps – SoftComply Risk Manager Quick Start Guide:
Hints
1. For a quick start, you can import risks to your newly created risk management project by using all the available import options that Jira provides. For detailed import guide of your existing risks, please look here.
2. You can navigate between risk views by using the left panel options: “Risk Management” (the table), “Risk Model” (setting your severity, probability and detectability scales, the risk levels and their range, and the matrices/RPN) and “Reports” (Risk Management Plan, Risk Management Report, Risk Table Report, Risk Matrix Report and Traceability Report).
3. First, customize the Risk Model according to your severity, probability and/or detectability levels, and assign the risk level values in the matrix cells and/or ranges in the RPN.
4. You can now start identifying your risks by entering risks and related information into the Risk Management table by filling in the table cells.
5. Link mitigation actions and verification actions by starting to type the Jira issue number or summary into the corresponding cells, and then selecting the required issue.
6. Customize the table (add, remove, edit columns) according to your needs by hovering over the table headers and selecting the options required.
7. Filter, sort and/or export the table content if necessary.
2. MANAGE RISKS
Risk Manager Plus is built to keep your data safe and secure. Each action is secured by a specific permission/project role. Before making any changes to a risk project, please review the setup of your risk project security/permissions. You can find the required permissions explained at Risk Manager Security.
2.1. Create a Risk Project
To manage risks you first need to create a special type of project in Jira. This is done by using the “New Risk Management project” menu item from the Risk Manager Plus drop-down menu on. The Risk Manager Plus knows whether it is a risk management project or any other project you have created to your Jira instance. Only risk management projects can have access to the features of the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus. In other words, in order to manage your product risks you first need to create a new risk management project.
Select from the Risk Manager Plus menu → Create “New Risk Management Project” and follow these steps:
1. The first step requires you to enter the project name, the project key and the project lead. These fields are the Jira standard fields that are required while creating a new project.
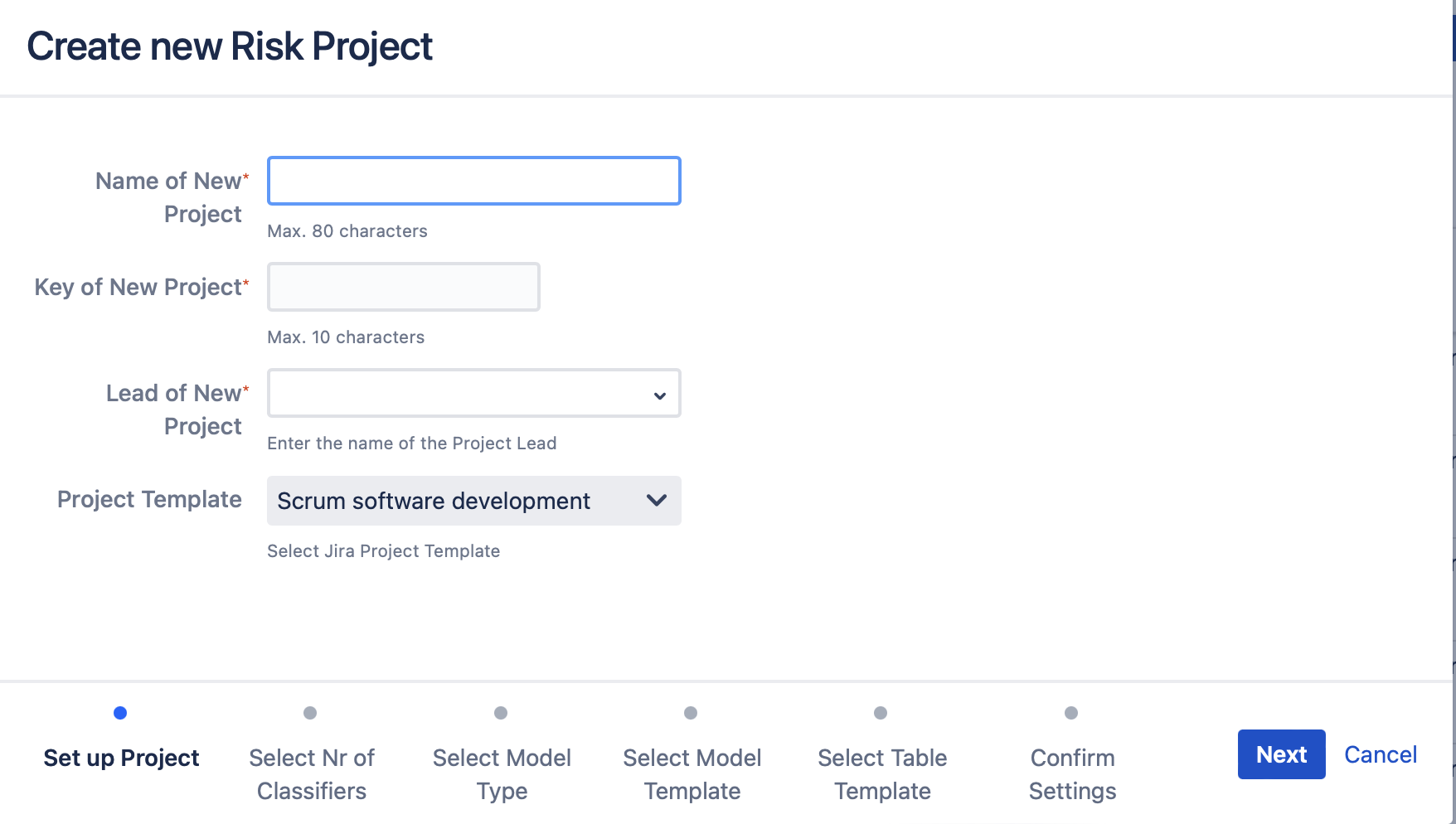
2. As a next step you can choose which parameters you are using for risk assessment – Severity and Probability (two (2) classifiers) or Severity, Probability and Detectability (three (3) classifiers):
3. Next, you can choose how risks are calculated and visualized, i.e. either in risk management matrices that have risk levels (“Risk Matrices with Risk Levels”) or in Risk Priority Number (“RPN”).
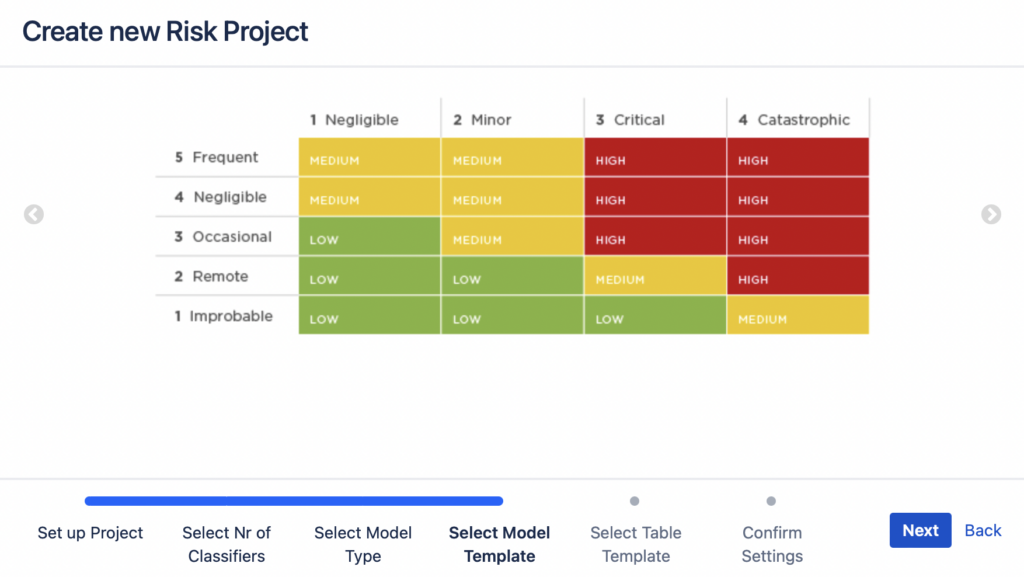
4. If you have chosen to use Risk Matrices with Risk Levels, you can choose the risk matrix size next. There are several of the most frequently used matrix layouts to choose from, as a starting point. You can, if you need to, customize your risk matrix after you have finished the project creation. Thus, to accelerate your risk management project setup, choose a matrix layout that is as close to your needs as possible to minimize customization effort later on.
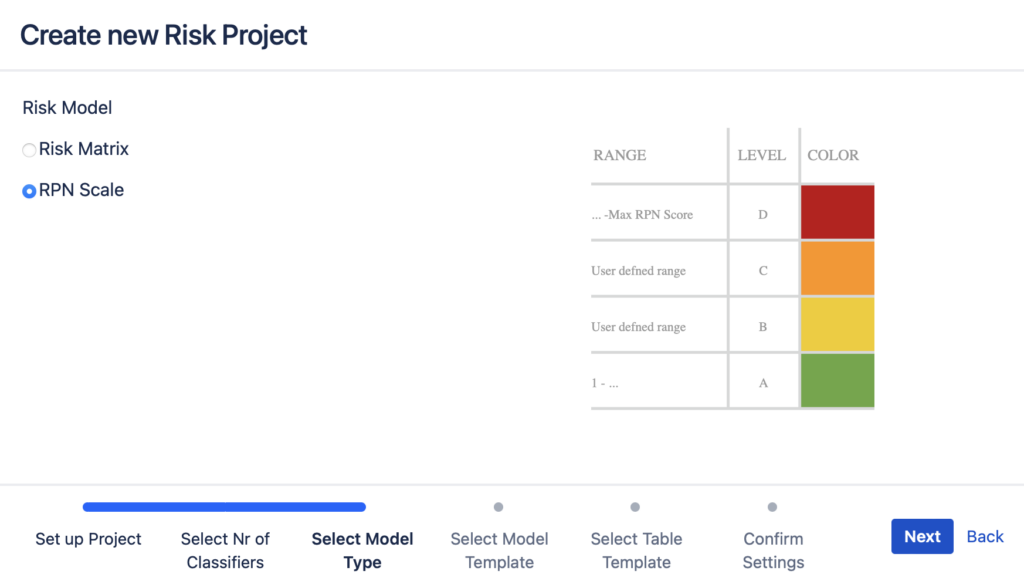
If you chose to go with RPN in the previous step, you can choose the number of Risk Levels and the FMEA scale next. Again, you can customize both of them after you have created the project but it is most time-efficient to choose options that are closest to your risk model. You are provided a choice between four or three risk levels and a combination of Severity, Occurrence and Detectability.
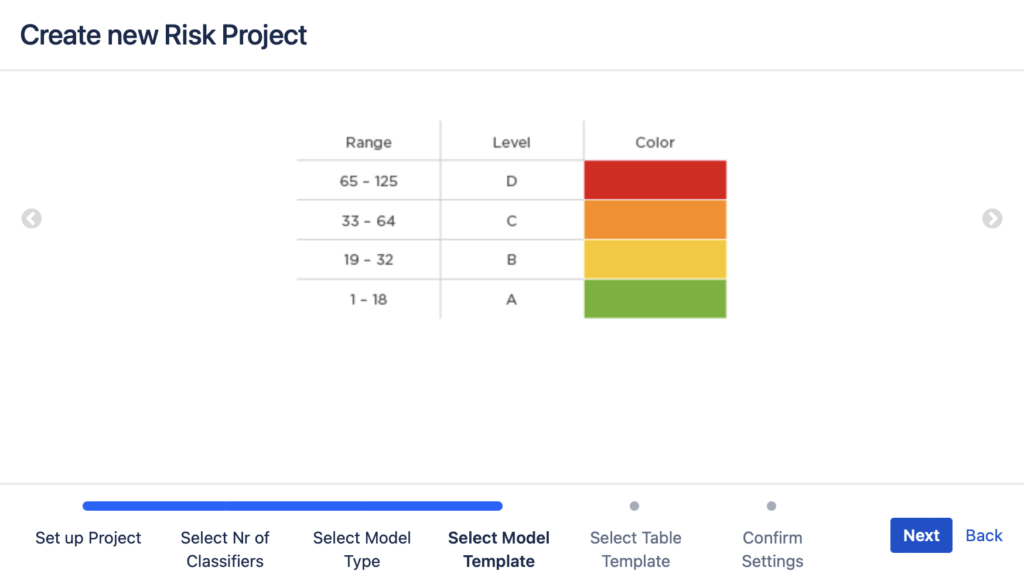
5. The final step of creating a new risk management project is the confirmation of the risk management method you chose.
NOTE! By default, for Hazard Anlysis and FMEA templates there is “Enable strict Harm and Severity mapping” enabled. This feature is related to the requirement of ISO 14971 for medical device risk management where one Harm is always having the same Severity throughout one risk project. That means, in case you update the Severity of a risk, the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus app will check all the risks in the risk project that have the same Harm and it will then update their Severity as well to keep the risk data consistent. In case you would like to use the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus to manage other types of risks (e.g. project risks, cybersecurity risks, etc) where you’d like to have different Severity levels for risks that have the same Harm, then you can disable this mapping in the Settings.
NOTE! You cannot delete the mandatory columns of Risk Summary, Harm, Severity (Initial and Residual) or Probability (Initial and Residual).
NOTE! If you have already created risk projects with the SoftComply Risk Manager before, you can now create a new risk project from an existing one.
You can do that by selecting the “Clone Project Configuration”- “Create new Risk Project from existing one” menu item from the Risk Manager Plus drop-down menu.
When you create a new risk project from an existing one you will be copying the risk matrix and risk table configurations into the new project together with the configuration schemes from the existing project. The risk data itself will not be copied to the new project.
Configuration can be customised after the new risk project has been created. The schemes that are being copied are the following: Issue Type Scheme, Permission Scheme, Priorities Scheme, Issue Type Screen Scheme. If you are using single or multi-select fields in the risk table with project specific options, please review the configuration of custom field options.
2.2. Configure the Risk Model
We would recommend you always start your risk project by configuring the Risk Model, i.e. before adding risks into the Risk Management table. Risk Model holds your risk project settings, i.e. scales for Severity, Occurrence/Probability and Detectability. It will also have RPN scale range settings and/or matrix settings. All settings are fully customizable.
You can see “Risk Model” on the left side menu, highlighted in the image below:
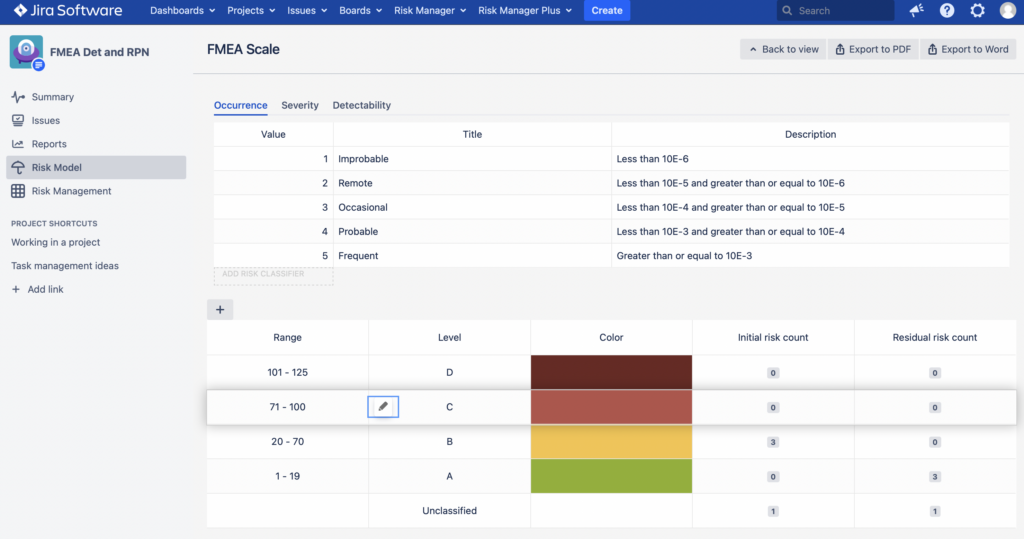
You can customise your Risk Model in RPN/FMEA by:
a) Adding/Removing severity levels and their descriptions (click on “Add risk classifier” below the Value column on Severity tab);
b) Adding/Removing occurrence levels and their descriptions (click on “Add risk classifier” below the Value column on Occurrence tab);
c) Adding/Removing risk class ranges (by “+” on top of the “Range” column);
d) Changing risk levels of the RPN scale.
You can customize your Risk Levels within your Risk Matrix by adding or removing severity and probability levels and their descriptions. To edit risk classes within a Risk Matrix, just hover over the risk class fields in the matrix and you will see the floating menu with available action buttons. It is important to be aware that if you remove a severity or a probability value, the risks that had the value assigned to them will automatically get the value of “unassigned”. You will need to re-evaluate those risks later on. In order to avoid this, it is best to configure your model and matrix before filling in your data in the risk management table!
Have a look at the short video tutorial below for Risk Matrix customization options:
2.3. Configure the Risk Management Table
Configuring the Risk Management table is the most important part of setting up your risk management project properly. Since each person responsible for risk management has their own way to approach risk management, it is best to use the risk terminology that is accepted and used in your company. The predefined templates are also a good option to start with if you have not yet created your own tailored approach. The columns/terms that are used are same as in ISO 14971. In other words, it is highly recommended to use one of our templates especially when you are working in a medical domain.
Below is a short video tutorial on SoftComply Risk Manager table customization options:
In order to change the table layout you have the following options:
1. Rename the column names and descriptions. This applies to all columns;
2. Add/Remove columns. You can create various different types of columns: Text area, Number, Date, Select, Multi Select, User, Version, Issue Link, Custom Field, and Component.
Note! You cannot delete the mandatory columns of Risk Summary, Harm, Severity (Initial and Residual) or Probability (Initial and Residual);
3. Hide columns. All columns of the table can be hidden to give a better overview of the table according to your needs.
4. Change the column order. You can change the order of the columns in your risk management table by clicking on the right/left arrows in the floating menu that appears when you hover over the column header.
5. Resize the column width. You can easily resize the width of each column by dragging the triangles on the headers of the column to expand or decrease the column width.
6. Sort the data by a column of your own choosing. Users can disable automatic sorting of data (default setting) and choose a column to sort the data in the table themselves.
You can access those actions by clicking on the menu that opens when hovering over the table header.
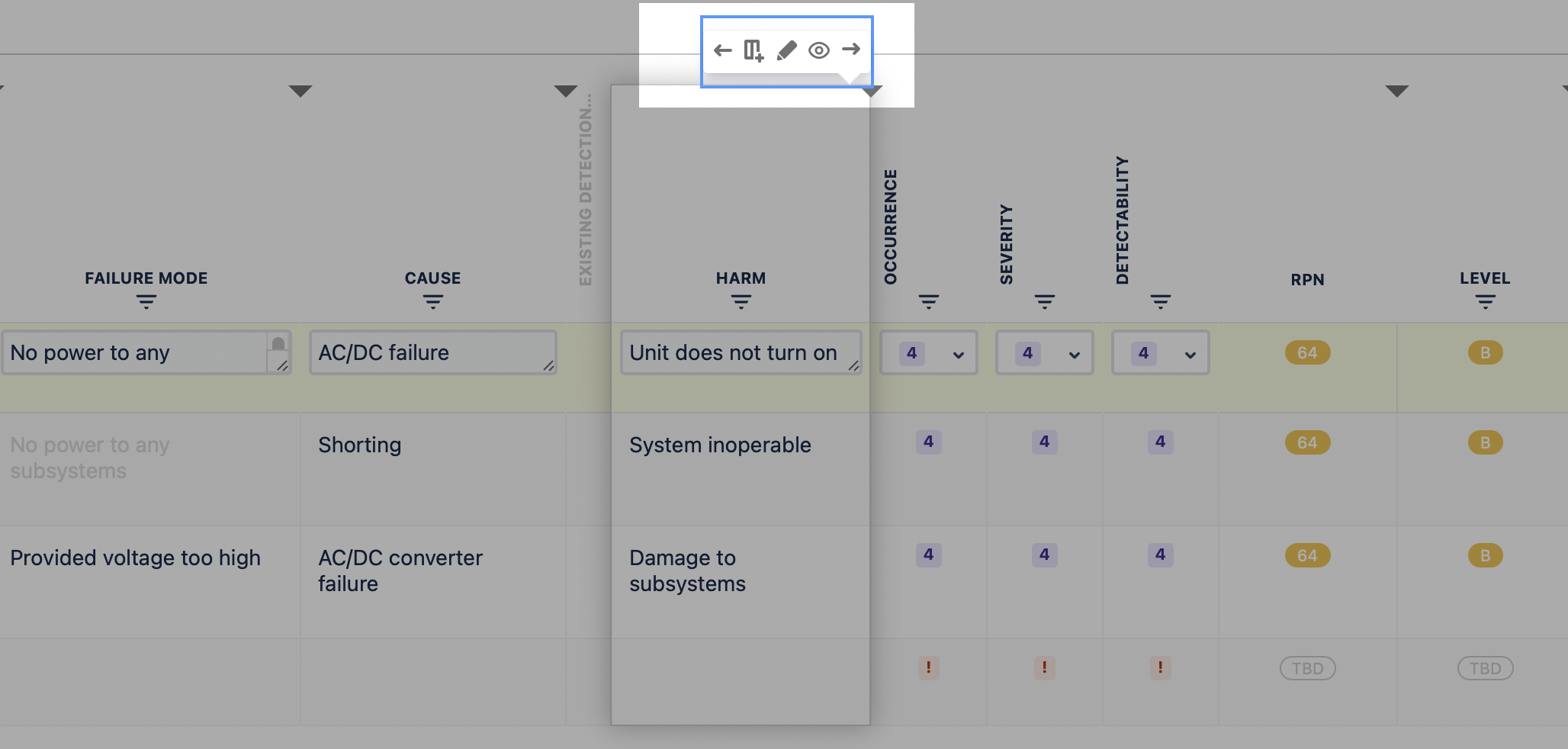
Editing options appear while hovering across the table with your mouse
2.4. Start Managing Risks
The SoftComply Risk Manager Plus is a tool to make risk management process easy to implement in your organization. Risk management is done by simply managing your risks in a table. Adding, removing, and linking risks to provide full traceability is now easier than ever!
The main tool for successful risk management is the risk management table. In the following sections you will learn how to get most out of its features
2.5. Add/Edit/Remove Risks
To add a new risk(s) there are three options:
1. Manually add risks by using the table’s first row; or
2. Clone risks from previous row; or
3. Import risks from another system or project
To add new risks click on “+ Add Risk” button above the table. This creates a top row of the table with empty values. Fill in the necessary column values and click on “Confirm” button that is found on the floating menu or press “Enter” on keyboard to save the risk.
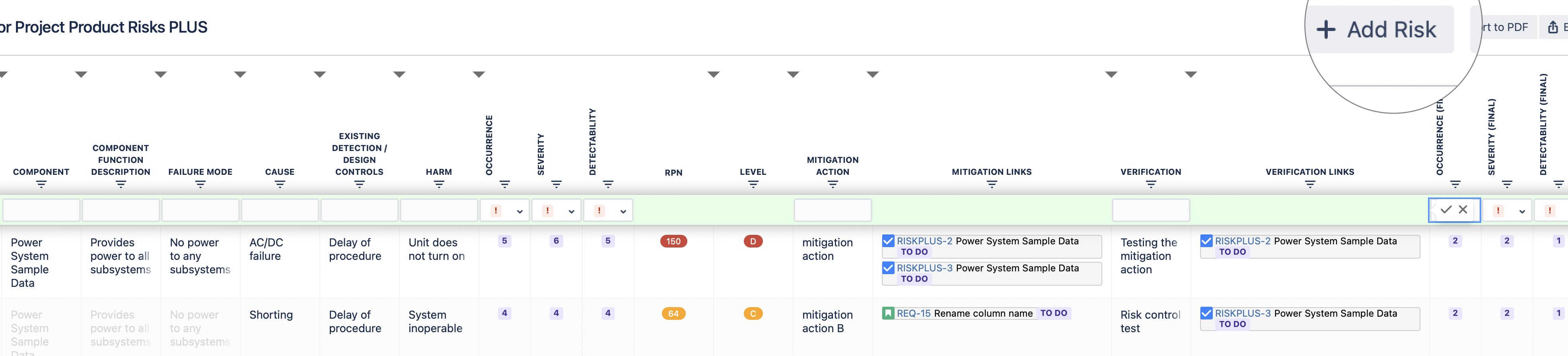
In order to add new risks the only mandatory field is “Hazard” in Hazard Analysis or “ID” in FMEA. All other fields can be left empty if you are not yet sure what to enter there.
Risk Cloning is a useful feature if you have more than one risk with the same Hazard, Hazardous Situation, etc. Often one Hazard can occur in different Hazardous Situations and can thereafter cause different Harms. Thus, by entering risks to the table, it would be convenient to copy all the values up to a certain cell, and then start filling in the rest of the necessary fields.
In order to do this, use the “Clone” feature. You can access the “Clone” feature from the floating menu. Be aware that it is important to select the “Clone” feature from the correct cell – the cell where you choose the “Clone” feature will be the last of the copied cells in the new risk management row that is created!

To edit a risk in the table, you have two options:
- First, by clicking a row that you would like to edit, makes the risk editable. Another click somewhere else in a table saves the changes you made and makes another risk (row) editable. If you have finished making changes, select “Confirm” on the floating menu;
- Second, by selecting “Edit” action from the floating menu.
You can also use keyboard shortcuts in the risk management table: to edit a risk, click on the cell you wish to edit. To save entered text in a cell, press “Enter”; to delete entered text in a cell that you added, press “Escape”. For saving a selected “Severity” or “Probability”, double-click “Enter” after selecting the desired level.
To delete or remove a risk from the table, select the correct risk from the table by hovering on it with a cursor. Then click on the “Delete” button of the floating menu. The risk itself will not be deleted! It will be changed from “Open” status of Jira issue workflow to the “Done” state. Thus, there is always an option to undo the delete action by opening the Jira issue view and manually changing the issue status back to “Open”.
In addition to manually entering risks to a table, you can also import risks from another system. If you have not yet added any risks to your project, then quick links to risk/issue import are available. If you choose to import risks from other systems (e.g. csv file, excel, other issue management systems) follow the instructions for this that Jira provides.
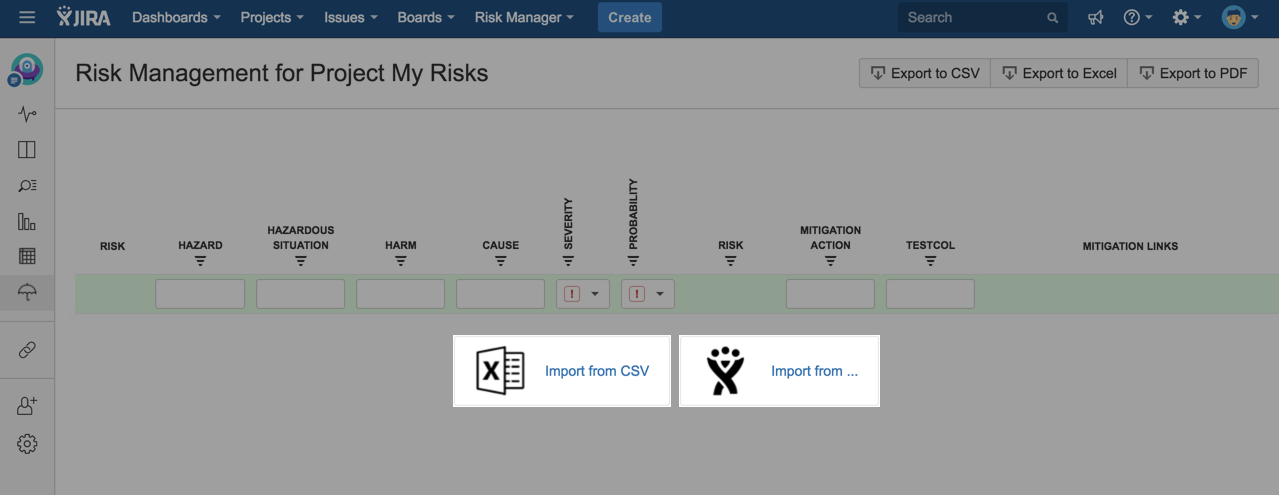
3. ASSIGN RISK CLASSES
3.1. Risk Matrices and Risk Classes
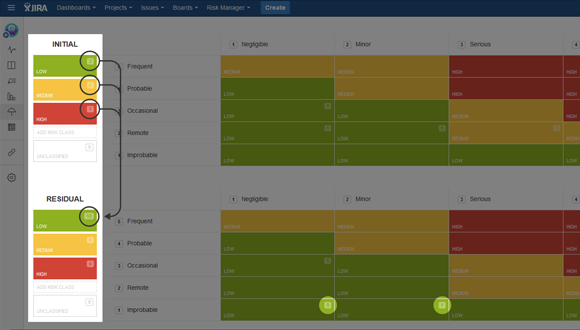
Assignment of risk classes (e.g. High, Medium, Low, TBD) is done automatically according to the risk matrix configuration after you have defined the values of severity and probability of the risk under assessment. The risk class of each risk under investigation will be assigned to each risk automatically based on the value of severity and probability of that risk. Risk class is defined in the risk matrix. Risk class cannot be assigned automatically to risks prior to defining the risk classes by setting the values of severity and probability. Until that time, the value of a risk class will remain “TBD” (To Be Determined).
According to the risk management process, each risk has two values of risk class assigned: initial risk class, and the final (residual) risk class after the mitigation has been completed. Thus, there are two values of severity and probability and two values of risk class columns on the risk management table corresponding to initial and residual risks.
The first column of the risk management table is called “Risk” and it provides a visual indicator of the initial and residual risk class values. E.g. if your initial risk class was High and you mitigated it to Low, then you should see a Red dot and a Green dot. This field provides a quick visualization of the risk mitigation results. The uncolored dot depicts a risk to which a risk class has not yet been assigned.
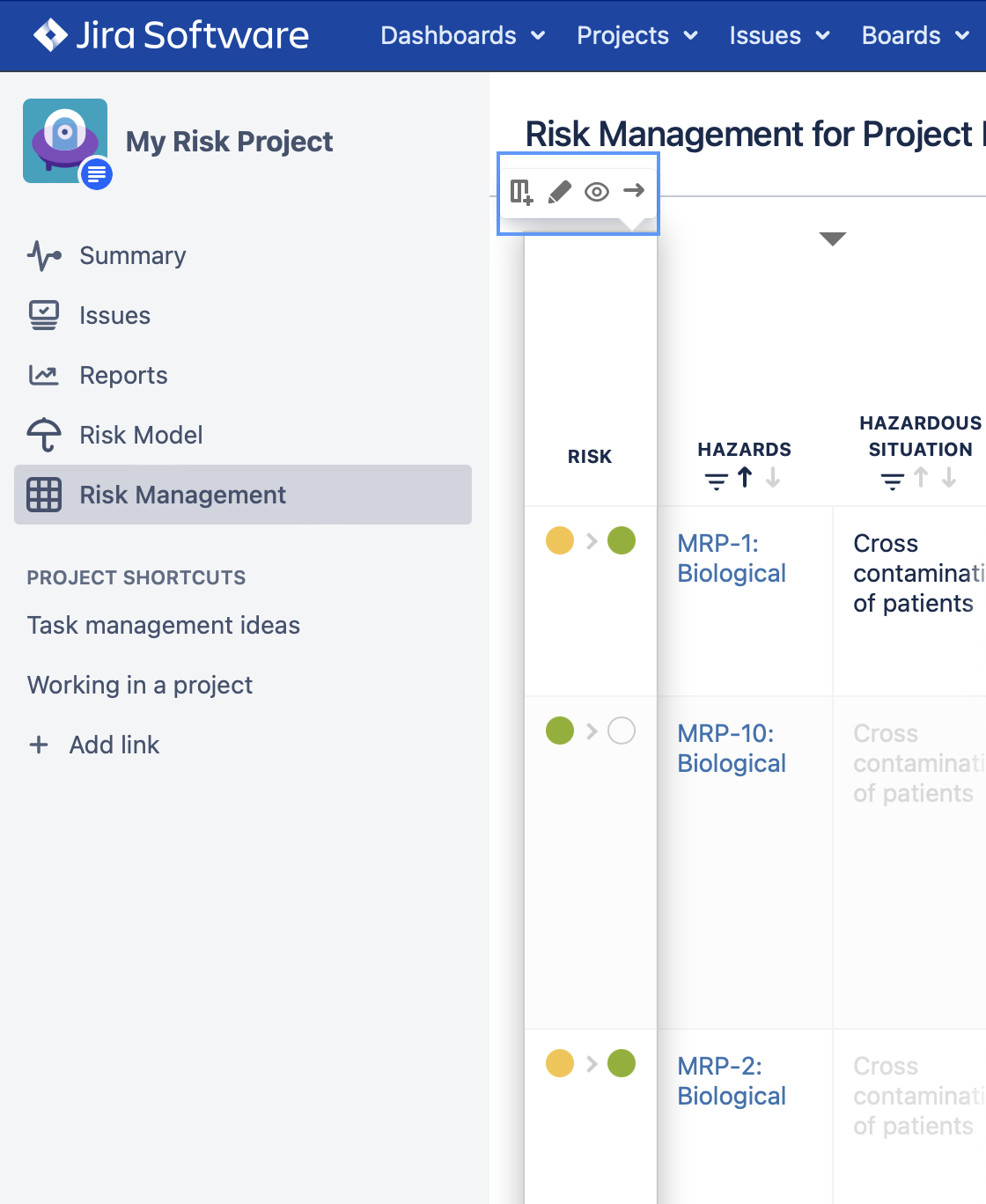
3.2. Risk Levels and RPNs (Risk Prioritisation Numbers)
Assigning of the risk ranges and risk levels for FMEA RPN are automatically done in the risk table according to the risk model configuration where you have defined the values of severity, occurrence and detectability together with risk ranges and levels for RPN calculation and visualization. RPN is calculated automatically based on the value of severity, occurrence and detectability you have assigned to the risk in the risk table. RPN value is “TBD” (To Be Determined) until you chose the values of severity, occurrence and detectability.
Similarly to Hazard Analysis, FMEA RPN has two values – an initial and a residual value where the initial RPN is that of the identified risk and the residual RPN is that of the risk after mitigation. In the risk table, you will therefore see the values of initial severity, occurrence and detectability first and the values for residual severity, occurrence and detectability once you have mitigated the risk. Similarly to Hazard Analysis, the first column of the risk table of your FMEA provides a quick visualization of the risk mitigation results, i.e. where the first dot illustrates the initial and the second dot the residual risk level.
4. MITIGATE RISKS
Risk mitigation can be done by assigning mitigation actions to your risks. The mitigation actions can be activities or procedures that mitigate the risk and lower the risk class. There are 2 columns that describe the mitigation actions:
- Mitigation Action (free text field), and
- Mitigation Links (link to another (external) issue/software item).
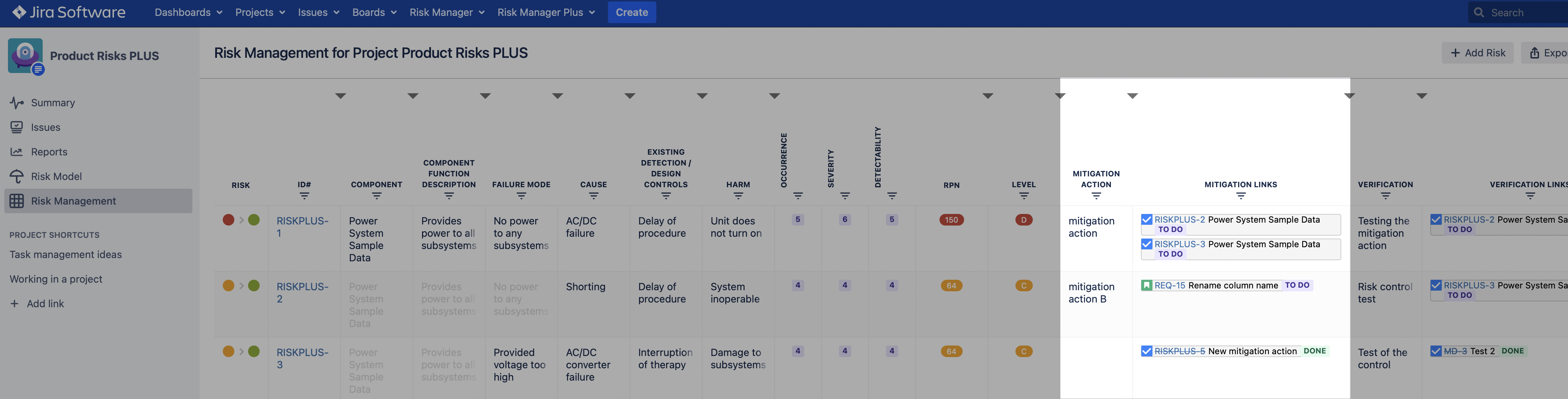
Mitigation actions can be defined either by entering a description to the column “Mitigation Action” or by linking another issue to the risk. Mitigation actions can be issues from other projects, thus you can link requirements or other development issues to the risk under mitigation. To link issues, start typing either an Issue key or Summary of the issue you would like to link to. The autocomplete text field will suggest you the issues it finds based on the text that you entered.
NB!: The recommended use of mitigation actions is as follows:
1. There should be at least 2 separate projects: one for the risk management and another where you manage other product development issues (like development tasks, requirements and alike that might be mitigation actions).
2. Link the mitigation action from the development project to your risk via “Mitigation Links” column.
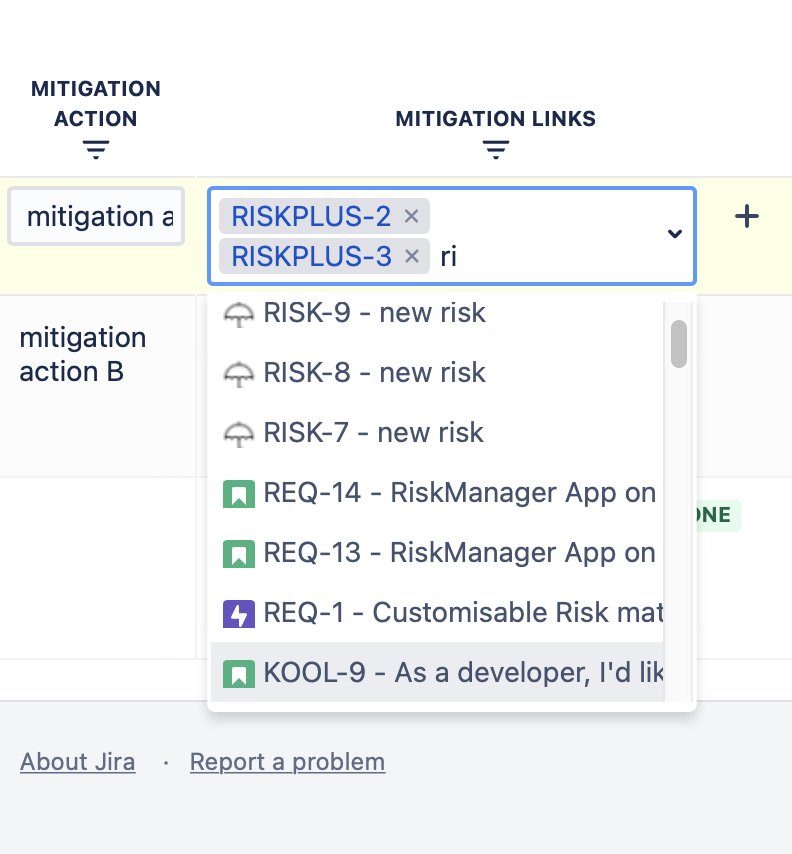
If you have no mitigation action defined yet, but you would like to create it during risk management project, then use “+” button in the Mitigation Links column. This will open a “Create new issue” popup window in JIRA and you can create a new mitigation action to any project you have access to. After creating an issue by using this feature, the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus automatically adds a link between the issue you created and the risk you were processing at that moment. Thus, you can add new risk mitigation actions and move on with your risk management from the same place you were at before.
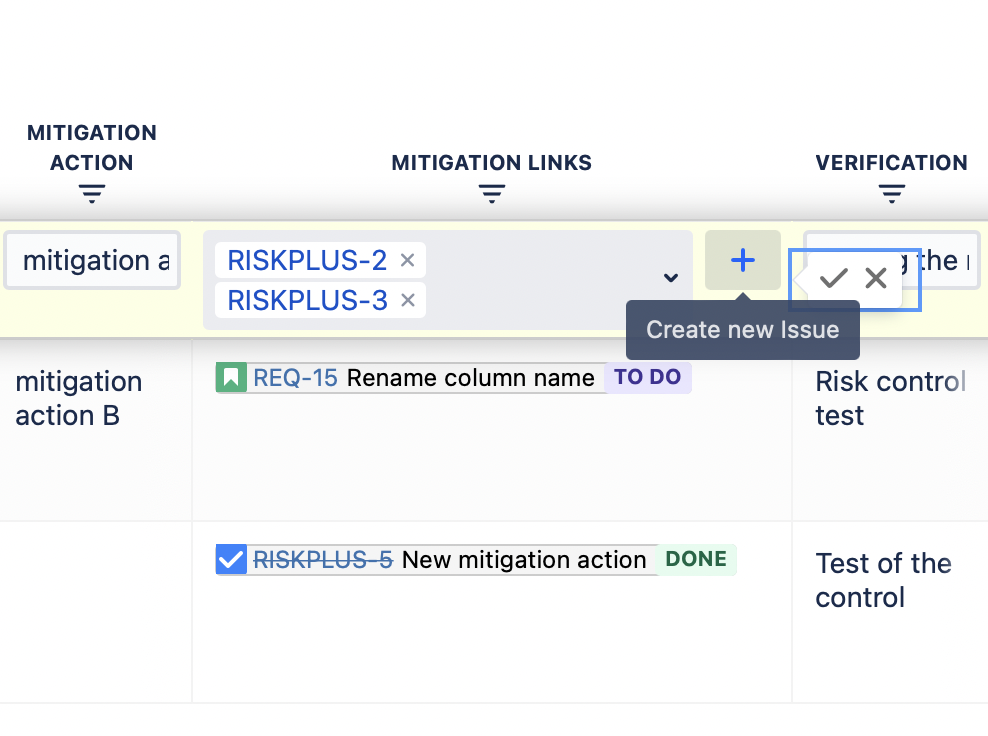
NB!: In the risk management table you can see the mitigation action issue key, issue summary and issue status. In this way, it is easy to assess at a glance if actions are done, in progress, or still on the to do list.
5. VERIFY MITIGATION ACTIONS
Verifying mitigation actions is similar to mitigating risks with regard to the features of the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus. There is always an option to add verification actions manually as a free text to column called “Verification Action” and linking the verification actions to the risk mitigation action (to verify that the risk mitigation action works as intended).
Linking verification actions (e.g. testing activities from another JIRA project) is similar to linking mitigation actions. It is best to start by typing the issue key or summary to autocomplete the text field and then pick the issue from the drop-down list of suggested issues.
By clicking on a “+” button on the right side of the “Verification Action” column, it is possible to create a new verification action in the risk management project. The created verification action will then automatically be linked to the risk.
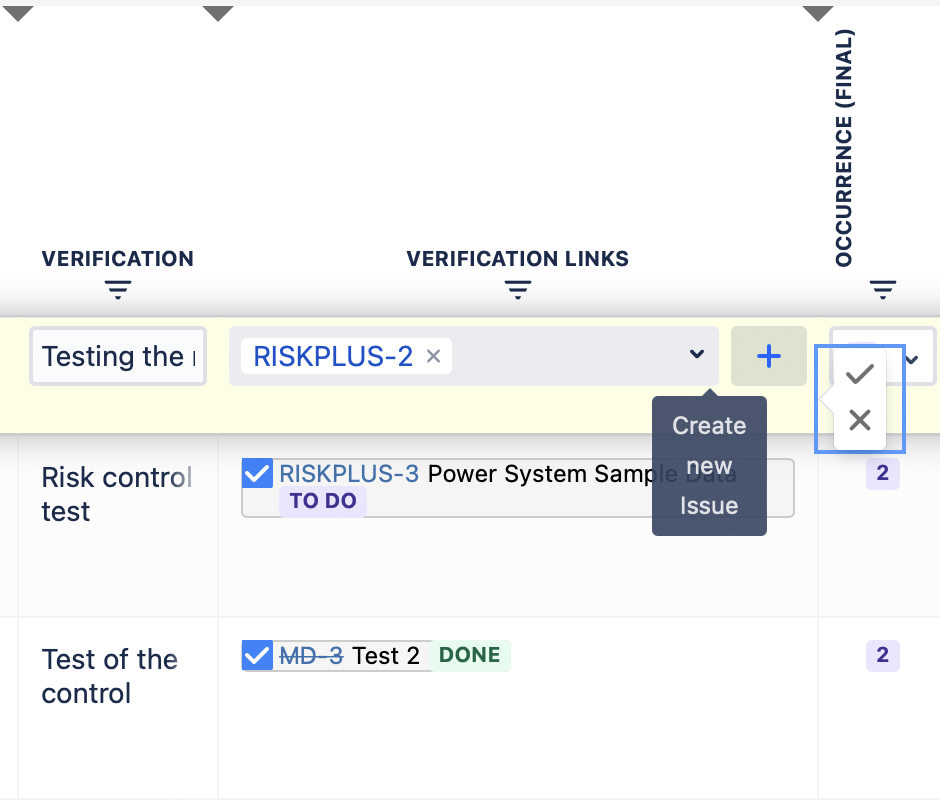
NB!: In the risk management table you can see the verification action issue key, the issue summary and the issue status. In this way, it is easy to assess if the verification actions are done, in progress, or still on the to do list.
6. ASSESS THE RESIDUAL RISKS
After mitigating risks, the final risk assessment should be conducted by assigning final severity, probability/occurrence and detectability values. Thereafter, the final risk will be calculated and it is possible to see the residual risk value in the risk management table. To see the initial and the residual risks click on the “Risk Model” icon on the left menu. You will see the Risk Matrix view for Hazard Analysis or the RPN view for FMEA. In the Initial Risk Matrix you will see the identified risks and their risk classes.
In RPN, you will see the initial risk count and residual risk count.
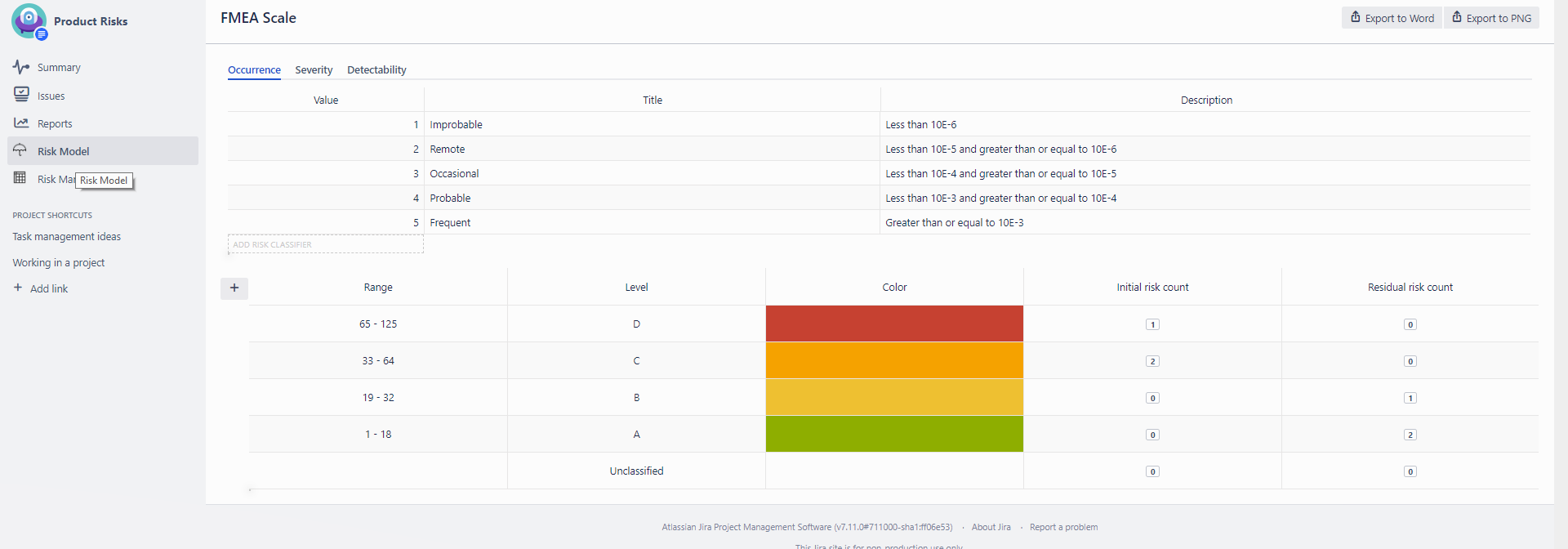
The matrices and/or the RPN table can be exported or printed by selecting the suitable action from the top-right corner of the page. It is possible to export the matrices to DOCX and PNG format. After exporting the matrices or RPN table, you can save the file as a snapshot of that moment in time.
It is also easy to visualize the effectiveness of your risk mitigation actions by looking at the first column of your risk management table. The coloured dots depict the values of the initial and the residual risk class of each risk. Thus, in a perfect world you wish to see primarily green dots on the right of the small arrow.
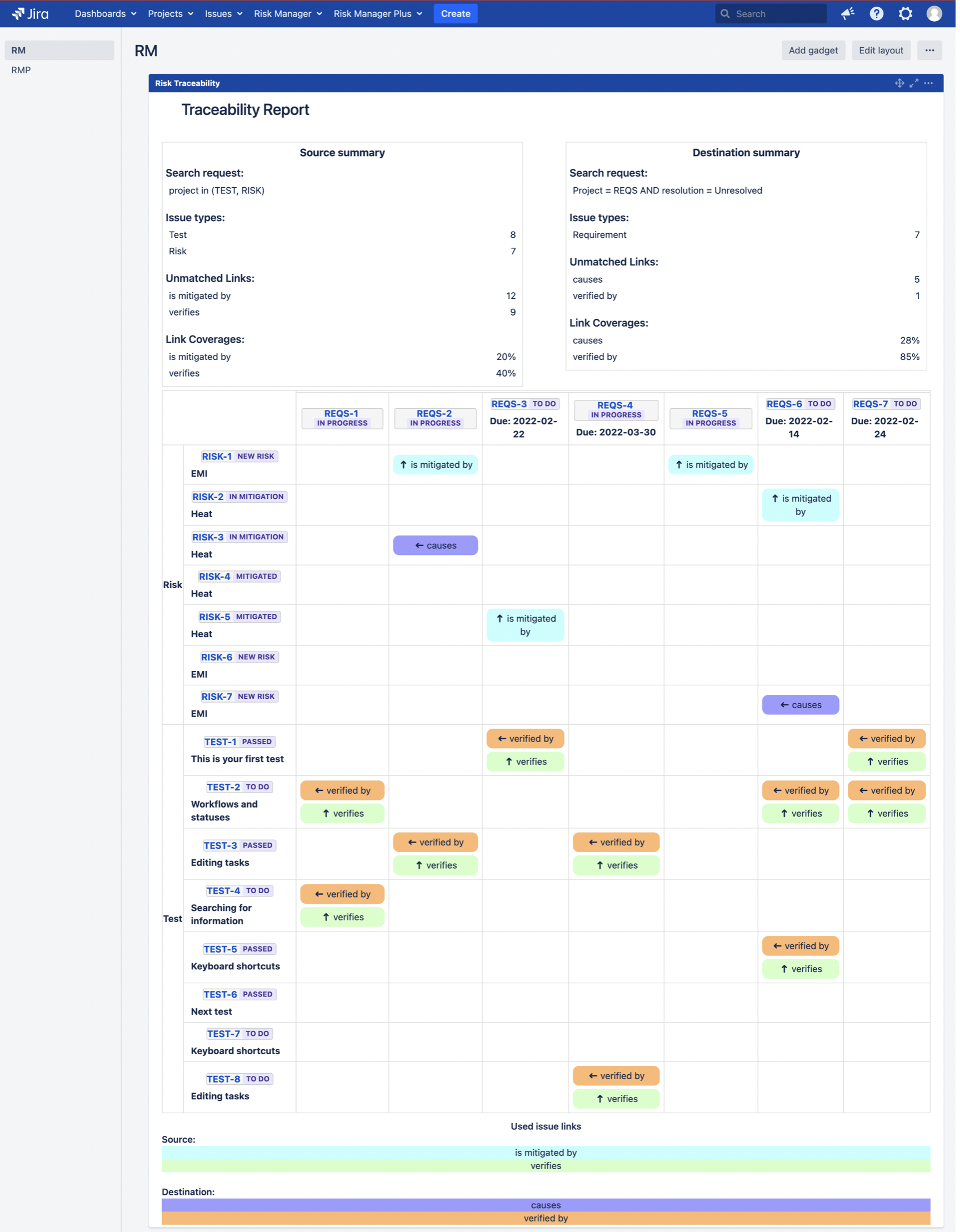
7. REPORT RISKS
The SoftComply Risk Manager Plus provides altogether six report templates – Risk Management Plan and Risk Management Report, Risk Table Report, Risk Matrix Report, Risk History Report and Risk Traceability Report.
The Risk Management Plan is based on the requirements of ISO 14971 giving an overview of all the planned activities of risk management.
The Risk Management Report is a document that describes the results of the Risk Management activities. Both reports can be accessed either from the Risk Manager Plus drop down menu or from the “Reports” section of JIRA sidebar.
Both the Risk Management Plan and the Risk Management Report include guidelines on how to fill in your project specific data. The Risk Management Plan automatically includes the data that you defined at the start of your risk management project, including the risk classes and their acceptance criteria; risk matrix or RPN configuration; the severity; detectability and the probability values. The Risk Management Report automatically includes the initial and the residual risk matrices and/or RPN table.
Risk Matrix and Risk Table Reports display the risk matrix and the risk table, respectively.
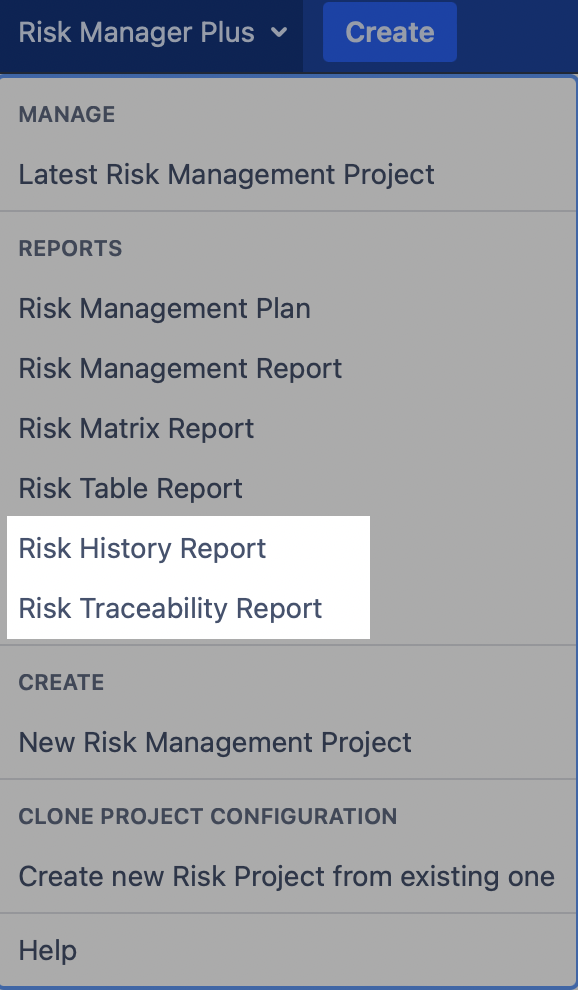
Reports can be selected from the top bar
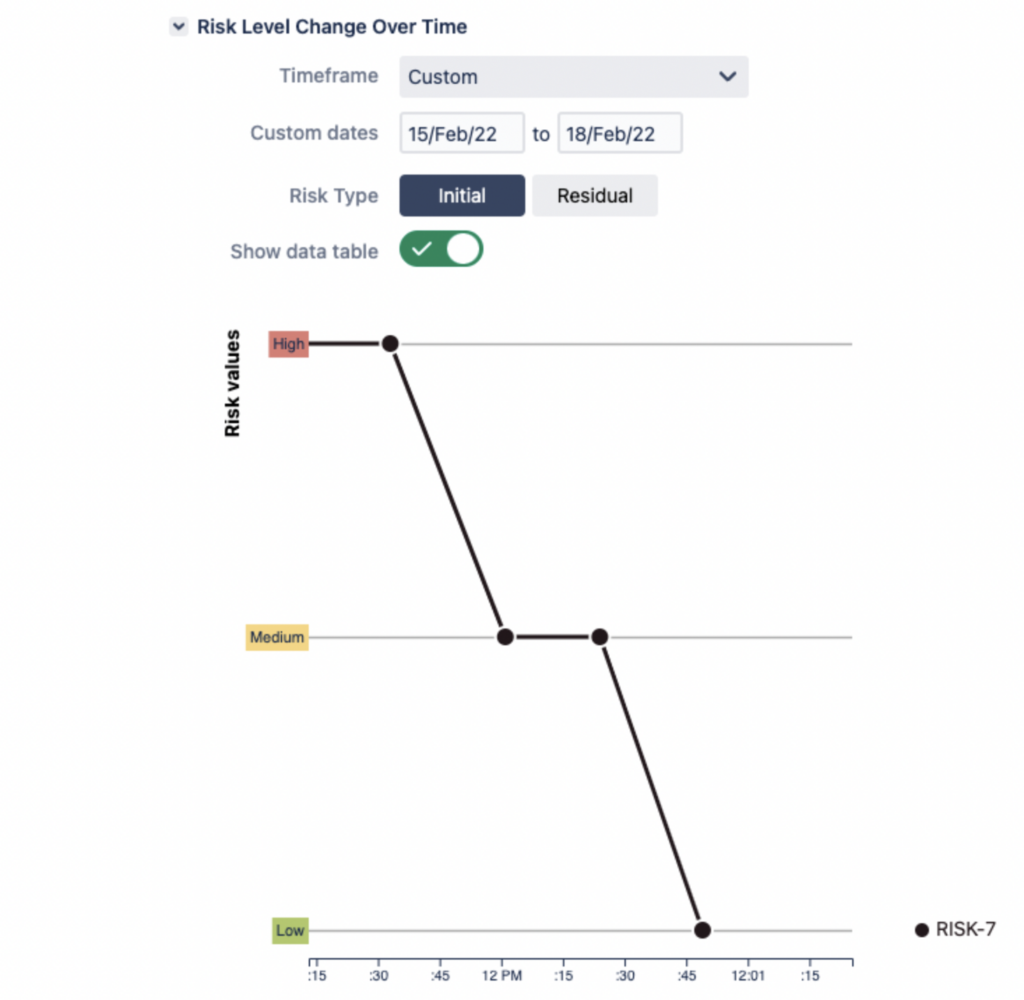
Risk History Report provides a graphical presentation of your risk assessment process over time:
Risk Traceability Matrix Report for a full overview of all the links to and from your risks as you want to display them, e.g. mitigation and verification actions.
8. BOOK A DEMO
To learn more about the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus, you are most welcome to book a DEMO CALL with the SoftComply team.
