P1 and P2
No we are not talking about the early Playstation versions…
ISO 14971 (2019 version, Annex C) indicates that the probability of a Harm occurring can be decomposed in two probabilities, P1 and P2, where:
P1 = Probability of Hazardous situation occurring
P2 = Probability of Harm occurring for a given Hazardous situation
The overall probability of a Harm occurring becomes then P = P1 * P2
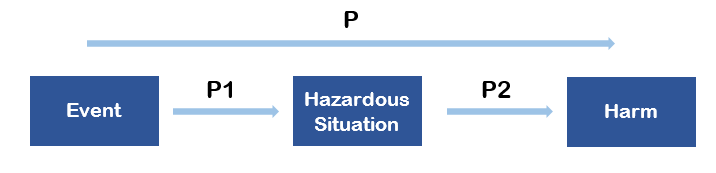
This decomposition is not mandatory and many companies use a single Probability value.
Advantages of Using this Approach
1. Separation of technical and clinical events
P1 is typically related to device failures or use errors. This is competence of the developers and engineer, who can give a good estimate (qualitative or quantitative) of a certain event occurring.
P2 is more related to the clinical aspects of the product. The probability of a patient or user being injured when exposed to a certain hazard can be better estimated by clinical specialists.
So, developers don’t have to “guess” the probability of a negative clinical impact and clinical specialists do not need to get involved in the technical aspects of the device.
2. Allocation of controls
Risk controls based on the design of the device have an effect on P1, i.e. they tend to reduce, or eliminate, the probability of certain failures occurring.
P2 is instead affected more by controls related to Protection and Information, i.e. mitigation by reducing or preventing the exposure of the patient / user to the hazardous situation.
A P1 * P2 approach is definitely favorable, in case technical and clinical events can be estimated separately with a good degree of accuracy. This is particularly valid for a combination device or devices that channel drugs. In this case the physiological and clinical effect of hazards such as overdose or underdose are well known and can be assessed independently.
An Example
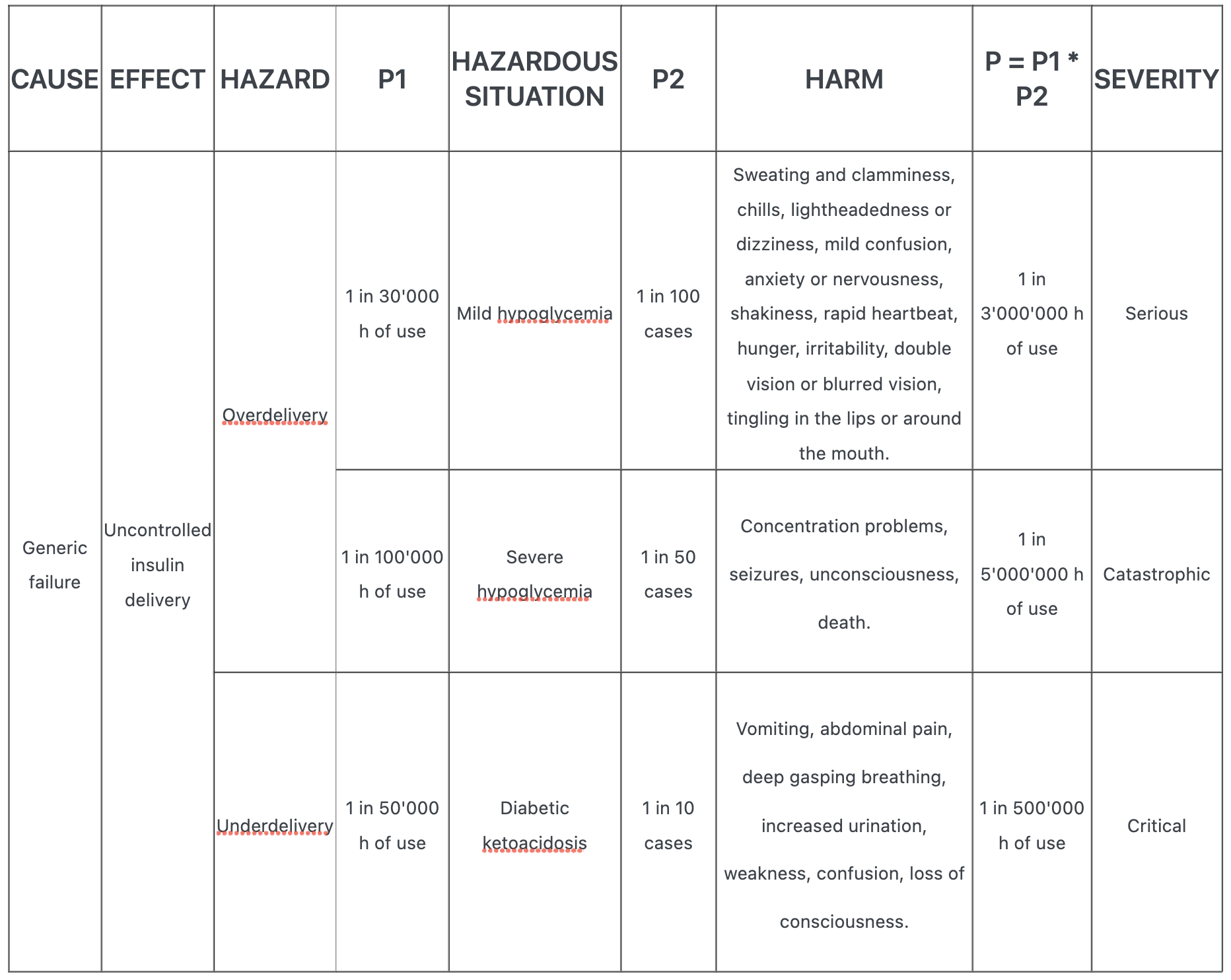
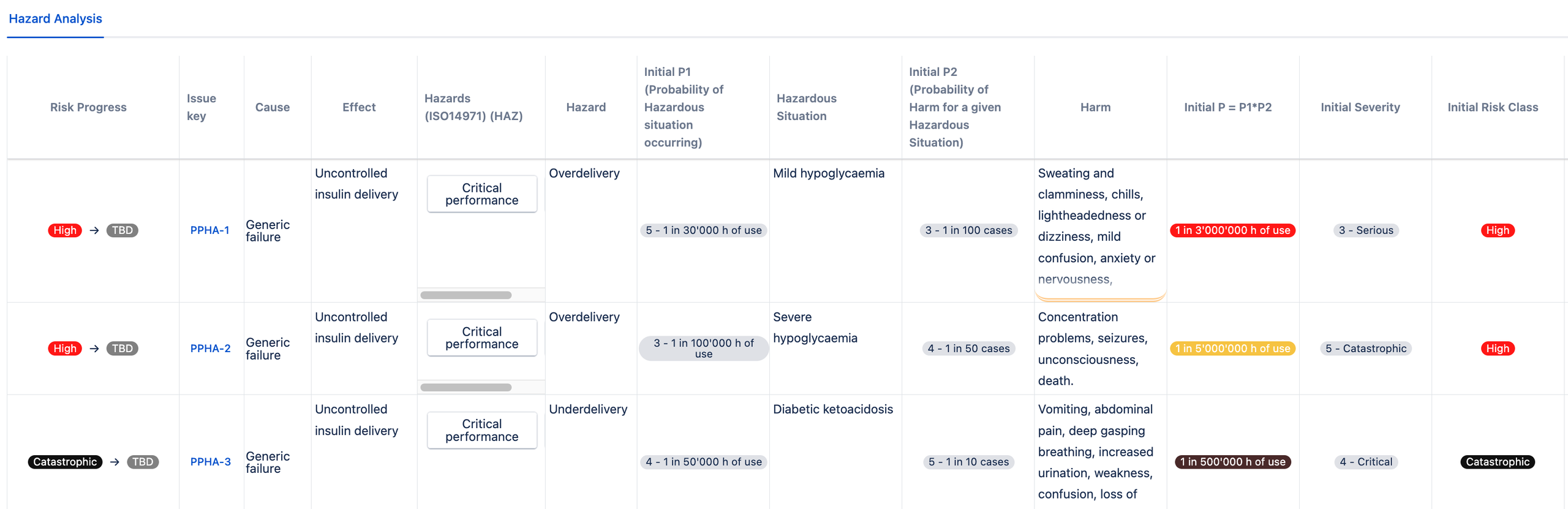
Following is an example of P1 * P2 approach of an insulin pump failing, where P1 is the probability of hazardous situation occurring and P2 is the probability of harm for a given hazardous situation.
One of the failures related to insulin pumps is the over delivery of the drug. This can result in (mild or severe) hypoglycemia. The underdelivery of insultin may result in diabetic ketoacidosis.
How to Implement P1 * P2 with SoftComply Risk Manager Plus in Jira Cloud?
SoftComply Risk Manager Plus is a Jira app developed specifically for medical device risk assessment that supports both FMEA and Hazard Analysis, automates traceability between risks, requirements and test cases, and generates compliant Risk Reports.
With the Risk Manager Plus, you can speed up the development of your risk assessment models and risk register by choosing a model or register from the several templates that come with the app. You can further modify the templates to your needs.
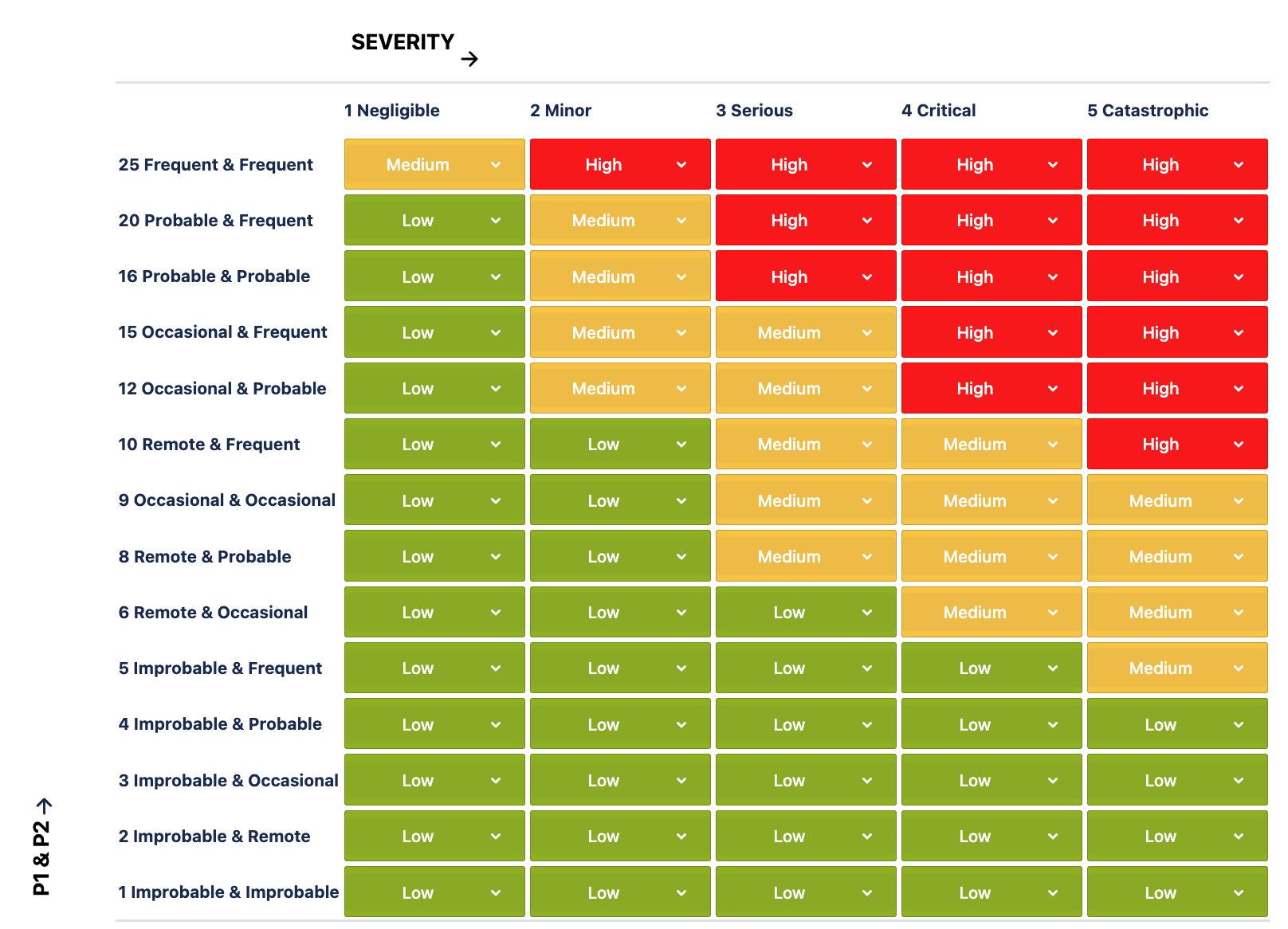
Among these templates, you will find a 3dimensional risk model template where P1*P2 have already been set up for you. You can customize the details further to map exactly to your risk management process. The 3dimensional risk model template with decomposed Probability on one axis and Severity on the other, and you can select the risk class directly in the risk matrix setting page:
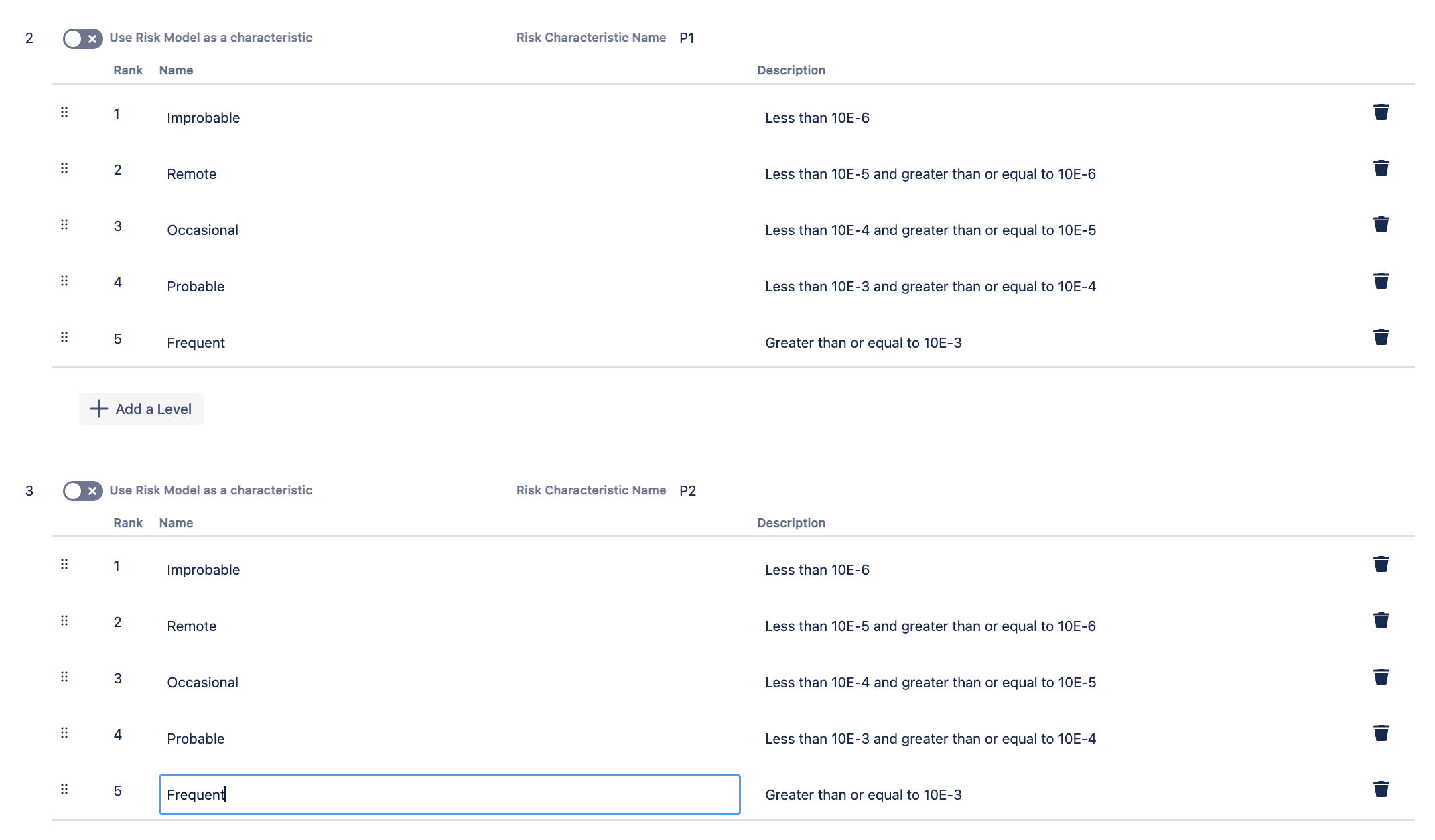
You can specify the sequence and the names for the levels and descriptions for both P1 and P2 on the settings page of the Risk Model after you have chosen the template.
Once the risk model is set up, you can choose the risk register template and start managing your risks in Jira with the risk model fields for probability and severity values already prepopulated for you:
You have now implemented the P1*P2 calculation in the SoftComply Risk Manager Plus on Jira Cloud!




